For working professionals
Domains
Doctorate
Artificial Intelligence
MBA
Data Science
Marketing
Management
Education
Law
Gen AI & Agentic AI
Doctorate
For All Domains
IIITB & IIM, Udaipur
Chief Technology and AI Officer ProgramSwiss School of Business and Management
Executive Doctor of Business Administration from SSBMEdgewood University
Doctorate in Business Administration by Edgewood UniversityGolden Gate University
Doctor of Business Administration From Golden Gate UniversityRushford Business School
Doctor of Business Administration from Rushford Business School, SwitzerlandGolden Gate University
MBA to DBA PathwayLeadership / AI
Golden Gate University
DBA in Emerging Technologies with Concentration in Generative AIGolden Gate University
DBA in Digital Leadership from Golden Gate University, San FranciscoArtificial Intelligence
Degree / Exec. PG
IIIT Bangalore
Executive Diploma in Machine Learning and AIOPJ Global University
Master’s Degree in Artificial Intelligence and Data ScienceLiverpool John Moores University
Master of Science in Machine Learning & AIGolden Gate University
DBA in Emerging Technologies with Concentration in Generative AIExecutive Certificate
IIITB & IIM, Udaipur
Chief Technology and AI Officer ProgramIIIT Bangalore
Executive Programme in Generative AI for LeadersupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from MicrosoftupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data AnalysisupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software DevelopmentupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial ExcellenceOffline Bootcamps
upGrad
Data Science and AI-MLMasters

Paris School of Business
Master of Science in Business Management and TechnologyO.P.Jindal Global University
MBA (with Career Acceleration Program by upGrad)Edgewood University
MBA from Edgewood UniversityO.P.Jindal Global University
MBA from O.P.Jindal Global UniversityGolden Gate University
MBA to DBA PathwayExecutive Certificate
IMT, Ghaziabad
Advanced General Management ProgramData Science
Degree / Exec. PG
O.P Jindal Global University
Master’s Degree in Artificial Intelligence and Data ScienceIIIT Bangalore
Executive Diploma in Data Science & AILiverpool John Moores University
Master of Science in Data ScienceExecutive Certificate
upGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from MicrosoftupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data AnalysisupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software DevelopmentupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial ExcellenceupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content CreationOffline Bootcamps
upGrad
Data Science and AI-MLMarketing
Executive Certificate
upGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from MicrosoftupGrad | Microsoft
Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content CreationOffline Bootcamps
upGrad
Digital MarketingManagement
Degree
O.P Jindal Global University
MSc in International Accounting & Finance (ACCA integrated)
Paris School of Business
Master of Science in Business Management and TechnologyGolden Gate University
Master of Arts in Industrial-Organizational PsychologyExecutive Certificate
Education
Education
Northeastern University
Master of Education (M.Ed.) from Northeastern UniversityEdgewood University
Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)Edgewood University
Master of Education (M.Ed.) from Edgewood UniversityDegree
Jindal Global University
LLM in Corporate & Financial LawJindal Global University
LLM in Intellectual Property & Technology LawJindal Global University
LLM in AI and Emerging TechnologiesJindal Global Law School
LLM in Dispute ResolutionGen AI & Agentic AI
Gen AI & Agentic AI
For fresh graduates
Domains
Software & Tech
Data Science
Management
Marketing
Software & Tech
Executive Certificate
International Institute of Information Technology, Bangalore
Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full StackupGrad | Microsoft
The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from MicrosoftOffline Bootcamps
upGrad
Full Stack DevelopmentData Science
Bootcamp
Offline Bootcamps
upGrad
Data Science and AI-MLManagement
Marketing
Bootcamp
upGrad Campus
Advanced Certificate in Performance MarketingOffline Bootcamps
upGrad
Digital Marketing- Study abroad
More
RESOURCES
BlogsCutting-edge insights on education
WebinarsLive sessions with industry experts
TutorialsMaster skills with expert guidance
Learning GuideResources for learning and growth
COMPANY
Careers at upGradYour path to educational impact
Hire from upGradTop talent, ready to excel
upGrad for BusinessSkill. Shape. Scale.
Offline CentresHands-on learning, near you
Experience centerImmersive learning hubs
About usOur vision for education
OTHERS
Refer and earnShare knowledge, get rewarded
Cyber Security Courses with Certifications
Cyberattacks are a global threat to organizations and individuals. lets learn how to safeguard against illegal access with a powerful Cyber Security system.

Cyber Security Certifications Overview
Cyberattacks pose a global threat to organizations and individuals, making cybersecurity a crucial field. A strong cybersecurity system protects against unauthorized access and malicious attacks. If you are interested in learning how to safeguard digital assets, enrolling in cyber security courses can help build essential skills.
Cybersecurity secures web-connected systems like servers, computers, and networks from cyber threats. It is widely used in businesses, financial institutions, and mobile computing. For those looking to start a career in this field, online cyber security courses offer a flexible way to gain knowledge and hands-on experience.
To understand basic cybersecurity, we can break it down into two parts—cyber, which involves data, networks, and technology, and security, which focuses on protecting them from threats. Many best cyber security courses cover both aspects, ensuring learners gain expertise in preventing cyberattacks.
As the demand for skilled professionals rises, earning cyber security certifications can boost career prospects. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, investing in cyber security training can provide valuable expertise.
Cyber Security tools include various apps and solutions capable of mitigating risks and safeguarding sensitive information against cyber threats.![]()
List of extensively used basic cyber security tools:
- Wireshark
- Nmap
- Web security
- Metasploit
- Ncat
- Aircrack-ng
- Entersoft Insights
- Nikto
- Cain and Abel
- Kali Linux
- John the Ripper
- Forcepoint
- PAROS proxy
- NMAP
- Truecrypt
- LifeLock
- Bitdefender
- TOR
- Malwarebytes
- Mimecast
- VIPRE
- SiteLock
A massive number of internet threats exist in cyberspace. Cyber threats like Malware, Viruses, Trojans, Scareware, Worms, Ransomware, etc., always intend to disrupt the sensitive information of individuals and organisations.
All organisations should know the amount of risk involved in each step in the cyber world. Hence, organisations must know the essential tools and methods to protect against cyber security challenges due to cyberattacks. Most organisations now include a dedicated team for handling cyberattacks.
Various tools are now available to defend network security and are implemented with the latest cyber security technology.
Let’s discuss the details of the critical cyber security tools and how to use them:
1. Firewalls
- Firewalls act as a security barrier between an organization’s internal network and external threats.
- They filter incoming and outgoing data to prevent malicious attacks.
- Learning how to configure and manage firewalls is a key part of many online cyber security courses, helping professionals secure critical systems effectively.
2. Antivirus Software
- Antivirus software detects and removes malware, spyware, and ransomware from IT systems. Regular updates ensure protection against evolving threats.
- Many best cyber security courses include training on antivirus management, equipping learners with skills to protect personal and business networks.
3. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- PKI ensures secure data transmission over the internet using encryption. It plays a key role in secure transactions and online communication.
- Professionals seeking to master encryption and authentication methods often pursue cyber security certifications to enhance their credentials.
4. Penetration Testing
- Penetration testing simulates cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities in security systems. Ethical hackers use this tool to strengthen security measures.
- Those interested in ethical hacking can enroll in cyber security training to learn practical techniques for conducting penetration tests.
5. Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
- MDR uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time.
- Organizations rely on MDR to prevent cyberattacks efficiently. Many cyber security courses online cover MDR solutions, providing learners with the latest security insights.
Understanding these tools is essential for cybersecurity professionals. If you’re considering a career in this field, researching cyber security course fees and choosing the right program can help you gain the necessary expertise to protect organizations from cyber threats.
It is essential to learn cyber security, but this learning is incomplete without understanding cyberattacks. The need for cyber security is perceived when cyberattacks begin stealing sensitive information of individuals or organisations.
A cyber attack is any effort to obtain illegal access to a computer, computer network, or computing system. The intention is to destroy, damage, or manipulate the computer system. Alternatively, the intention can be to modify, delete, block, steal or manipulate the data stored in the systems.
Those individuals or groups who undertake cyber security attacks are known as cyber criminals. Usually, they are referred to as hackers, malicious actors, actors, and hackers. Cybercriminals can be individuals who implement their computer proficiency to perform malicious attacks. In some other cases, cybercriminals can be those working with other malicious actors in a criminal association to detect vulnerabilities or issues in computer systems. These vulnerabilities can be exploited for personal financial gain.
Cyber security attacks can arise from government-endorsed troops of computer experts. They are known as nation-state attackers.
Reasons behind the occurrence of cyber attacks:
Cyber attacks can have different objectives like
1. Financial gain:
Most cyberattacks (specifically those against commercial bodies) intend to have financial gain. These cyberattacks usually target to steal sensitive data like employees’ personal information or customers’ credit card numbers.
Cybercriminals access goods or money using the victims' sensitive cyber security information. The sensitive information can be property information or critical corporate data. By spying on valuable data of individuals or corporates, cyberattacks deceive them and ask for money.
2. Revenge:
Malicious actors can undertake cyberattacks especially to spread confusion, chaos, dissatisfaction, or mistrust. They usually undertake these actions to obtain revenge for acts implemented against them.
Cybercriminals can aim to publicly humiliate the attacked parties or to disrupt the organisations' status. These attacks in information security are usually targeted at government entities. However, they can also target nonprofit organisations or commercial bodies. Nation-state attackers can be responsible for cyberattacks meant to take revenge.
3. Cyberwarfare:
Not only malicious actors but even Governments across the world are involved in undertaking cyber attacks. Many national governments are suspected or acknowledged for designing and performing attacks against other nations. The reasons can be continuing economic, political, and social clashes. They are known as cyberwarfare and they are one of the key reasons behind attacks on information security.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
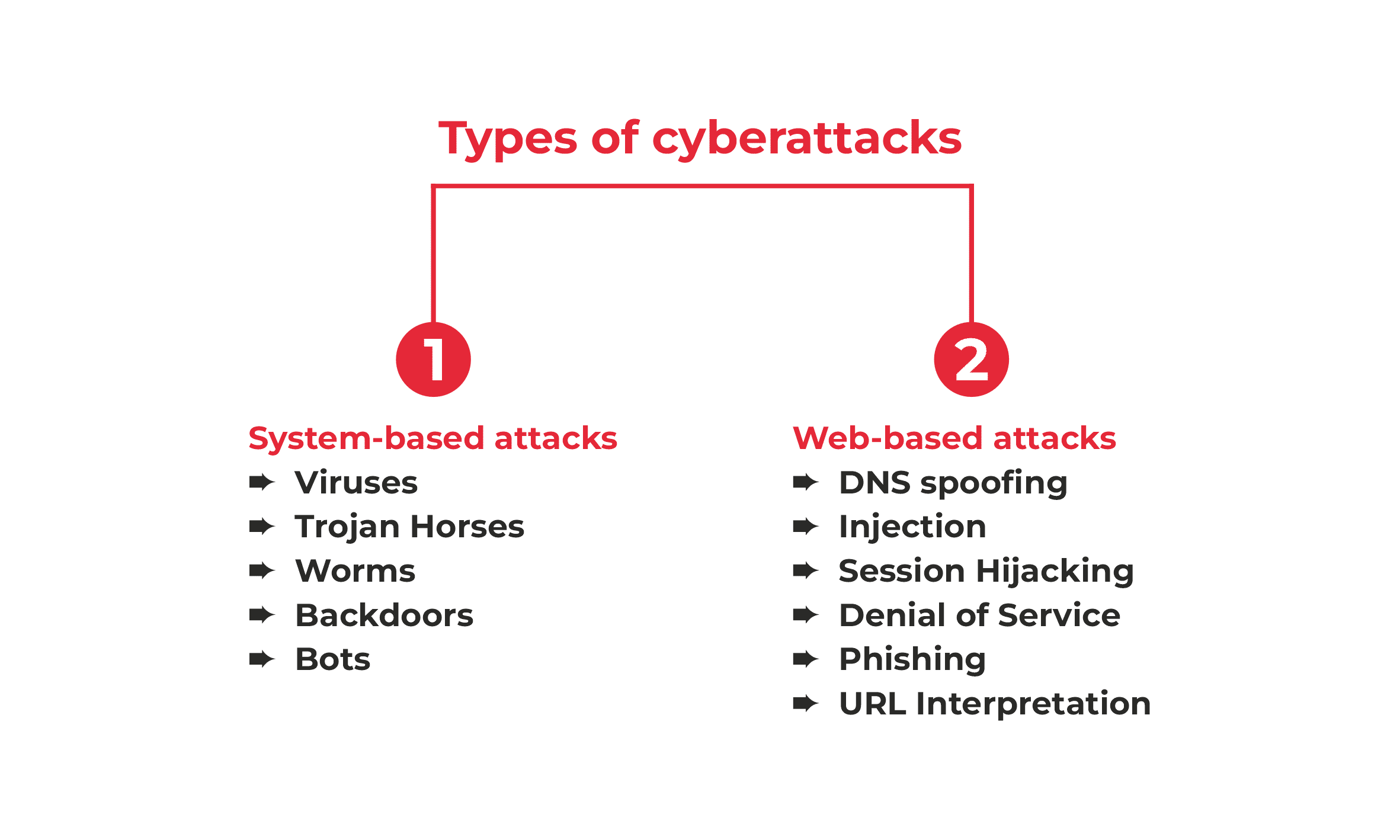
1. System-based attacks:
They intend to compromise a computer's security or network. A few of the prevalent system-based attacks are Viruses, Trojan horns, Worm, Backdoors, and Bots.
2. Web-based attacks:
They take place on a website or web app. Few of the prevalent web-based attacks are:
- DNS Spoofing
- Injection attacks
- Session Hijacking
- Denial of Service
- Brute force
- Phishing
- Man in the middle attacks
- Dictionary attacks
- Protocol attacks
- File Inclusion attacks
- Application layer attacks
- URL Interpretation
How to Avoid a Cyber Attack?
Here are the best practices to avoid a cyber attack:
- The use of software (for example –antivirus software) to safeguard the system against malware. It adds another layer of security against cyberattacks.
- Executing perimeter defenses like firewalls to block attack attempts and also block access to acknowledged malicious domains.
- Deploying proper security configurations, user access controls, and password policies.
- Preparing incident response plans to resolve a breach.
- The use of a patch management program to work on the acknowledged software vulnerabilities which can be misused by hackers.
- Teaching individual users about attack circumstances and how they can protect the network security of an organisation.
- The use of a monitoring and detection program to recognize and alert mistrustful activity.
In cybersecurity, a threat is a malicious activity an individual or institute undertakes. The intention behind the same is to corrupt or steal data, obtain access to a network, or disturb digital operations. All cyber threats aim to arouse vulnerability in cyber security
The cyber community outlines the following cyber security threats that create vulnerability in cyber security:
1. Malware:
Malware is malicious software and is popular as the most widespread cyber-attacking tool. It is the most prevalent type of cyber attack wherein hackers or cyber criminals use malicious software to damage or interrupt a genuine user's system. Usually, malware spreads through an illicit email attachment or a download link that appears legitimate but actually not. Malware intends to illegally earn money or could have a political intention.
The significant types of malware are:
- Virus
- Trojans
- Spyware
- Ransomware
- Adware
- Botnets
- Worms
2. Phishing:
In phishing, people receive emails from a cybercriminal that appear to be coming from a legitimate company (like eBay, PayPal, financial institutions, friends, co-workers, etc.) asking for sensitive information like personal data or credit card details. Subsequently, it deceives them for monetary gain.
Phishing in cyber security implies that cybercriminals contact a target or targets through phone or email or text message through a link. This kind of link persuades them to click and ultimately deceives them. The link redirects them to deceitful websites to submit sensitive data like personal information, credit card and banking information, usernames, passwords, and social security numbers. Clicking on the link instals malware on the target devices too. As a result, hackers can remotely control devices.
3. SQL Injection:
In this form of cyberattack, cybercriminals abuse vulnerability in computer-controlled applications. They insert malicious code in a database through a malicious SQL statement. So, they compromise cyber security information to steal or access sensitive information and control the database.
Once the cyberattack accomplishes, the malicious individual can observe, modify, or delete private details of customers, sensitive company data, or user lists stored in the SQL database. The need for cyber security is extremely realised at this point when cybercriminals are accessing sensitive data.
4. Denial-of-service attack:
In this category of cyber security threat, a cybercriminal disallows a computer to fulfil authentic requests. It destroys the targeted servers, networks, and services with traffic and makes the system unstable. Moreover, it disallows an organisation to manage its vital functions.
The requests originate from numerous IP addresses making the system unstable. Furthermore, it slows down the network speed, makes them temporarily offline, overloads their servers, and stops an organisation from performing its key functions.
5. Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack:
In this type of cyber threat, a cybercriminal interrupts data transfer or conversation between two parties for robbing the data. When cybercriminals come in between the two parties, they appear like honest participants. So, they can gain sensitive information and return various responses.
The key objective of a MITM attack is to obtain access to your organisation or customer data. This cyber threat compromises cyber security measures, for example, a cybercriminal can interrupt data flowing between the network and the target device on an insecure Wi-Fi network.
6. Advanced Persistent Threats (APT):
An APT occurs when a malicious individual or organisation obtains illegal access to a network or system and stays unnoticed for an extended period.
7. Brute Force:
This cryptographic hack implements a trial-and-error method to estimate all possible combinations until precise information is discovered. Typically, cybercriminals use this form of cyber security threat to gain personal information regarding encryption keys, login credentials, targeted passwords, and Personal Identification Numbers (PINS).
8. Domain Name System (DNS) attack:
In DNS attacks, cybercriminals use the faults in the DNS (Domain Name System) to readdress site users to malicious sites. After redirecting them, cybercriminals steal data from the affected computers. The DNS system is a vital component of the Internet infrastructure because a DNS attack is a severe cybersecurity threat.
The common sources of cyber security threats are -
- Hackers
- Terrorist Groups
- Criminal Groups
- Hacktivists
- Corporate Spies
- Malicious Insiders
Cybercrime is an illicit activity that targets or uses a computer/computer network/networked device. In other words, Cybercrime is the illegal treatment of any communication device to simplify the occurrence of any illegal activity. The use of the latest cybercrime security is inevitable to curb cybercrime.
Cybercrimes can target individuals, business groups, and governments. Hackers or cyber criminals commit most of the cybercrime in the lure of money. In most cases, cybercrime targets impairing computers for personal or political profit.
Individuals or organisations can carry out cybercrime. Cybercriminals are exceptionally technically proficient and use cutting-edge techniques, whereas others are beginner hackers.
Phishing, malware attacks, and Distributed DoS attacks are the prime contributors to cybercrime. To understand the relationship between cybercrime and security, let’s first understand the types of cybercrime:
Types of Cybercrime:
The below list highlights specific examples of various types of cybercrime:
- Internet and Email fraud
- Identity fraud that soles and uses personal information
- Stealing of financial or card payment data
- Robbery and trade of corporate data
- Cyber Extortion (demands money to avoid a threatened attack)
- Ransomware attacks (a category of cyber extortion).
- Cyber Espionage (hackers access company or government data)
- Cryptojacking (hackers mine cryptocurrency using resources they don’t own)
- The practice of shutting down or misusing a website/computer network
- Spreading hate through hate speech and stirring terrorism
- Open images of children that spread pornography
The majority of cybercrimes fall under two categories:
1. Targeting computers:
This category of cybercrime implements the best possible cyber security measures to harm computer devices. Examples include denial of service attacks and malware.
2. Using computers:
This category uses computers to carry out all the categorizations of computer crimes.
A firewall in cybersecurity is a network security tool that monitors incoming and outgoing traffic to protect against external threats. It follows a set of security rules to allow or block data packets, preventing malicious activities such as hacking and viruses. Learning about firewalls and their role in cybersecurity is essential, and cyber security courses online provide in-depth knowledge of how they work.
Firewalls act as a protective barrier between internal networks and external sources, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed. Professionals looking to enhance their cybersecurity skills can benefit from the best cyber security courses, which cover firewall configurations and network security strategies.
One of the best firewalls to use is the Windows Defender Firewall. This firewall in cyber security provides multiple configurable settings including -
- Manually block a program
- Choose to let apps pass data
- Turn off the firewall
The following steps let you use this firewall to alter the Windows Firewall Settings:
Step-1: Type ‘Windows Defender’ in the Search region of the Taskbar and choose ‘Windows Defender Settings’ from the shown list.
You can do various things from the ‘Windows Defender Firewall’ area. The left pane shows the option to Turn Windows Firewall either On or Off.
Note: It is recommended to check here frequently if the firewall is enabled or not. Certain malware, if caught by the firewall, can turn off without informing you.
Step-2: Click to verify which firewall is enabled and then with the back arrow, you can come back to the main firewall screen. It is possible to restore the defaults if you changed them.
The ‘Restore Defaults’ option in the left pane provides access to these settings.
Note: Settings labelled with a blue & gold defence need an administrator-level password for access.
Here are some prominent applications of a firewall that users must understand to safeguard their system:
![]()
- Avoids illicit remote access:
Myriad unethical hackers are making continuous efforts to gain access to vulnerable systems. The unaware user is unaware of who can access their system and data. Using a powerful firewall avoids any possibility of a potential unethical hacker gaining remote access to a system.
- Avoids the flow of unsolicited content:
In the absence of a strong firewall, unsolicited content can easily penetrate a system. The majority of the operating systems will be equipped with a firewall that will look after the unwanted and malicious content from the Internet.
Every time a new system is put into place, the user should check whether a firewall exists or not. If it does not exist, the third-party firewall needs to be installed.
- Avoids offensive content:
A lot of youth and adolescents are exposed to immoral content on the Internet. Exposure to any form of content featuring offensiveness can be harmful to their young minds. Consequently, it leads to weird and immoral behaviours. The use of a powerful firewall defends computer systems because it can avoid access to immoral and offensive content. Therefore, the use of firewalls lets parents keep their children safe.
- Avoids damaging content from online videos and games:
Plentiful sites allow watching and downloading movies. Also, plentiful sites allow playing and downloading the games. Certain movies and game sites have destructive content in form of viruses and malware. This content tries to penetrate the user’s system. So, your system should be equipped with a firewall because it ensures constant protection of your system from potential malware attacks from online videos or games.
- Promises security based on Protocol and IP Address:
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a kind of firewall that defends the systems from those elements which are outside the network of the system. Consequently, these systems’ IP addresses are detectable only in their network. So, their systems stay safe.
- Safeguards conversations and coordination contents:
Organisations involved in service industries need to constantly interrelate with third-party clients. Most of the content from such coordination undertakings is confidential. It should be effectively protected.
No organisation can compromise the expense of leakage of this kind of important content. A firewall not only safeguards the systems but also enables a safe flow of data.
- Ensures seamless processes in organisations:
Organisations are hugely dependent on enterprise systems and software. For example, using credentials, users can log in to their systems from any system in the network. Without a firewall, it can be quite challenging for organisations to implement seamless operations.
- Protects against data breaches and cyberattacks for businesses
- Protects both data and network security
- Illicit user access is prevented
- Offers a faster recovery time after a breach
- Offers end-user and endpoint device protection
- Supports Regulatory adherence and Continuity of operations
- Facilitates employees To work safely
- Cease your website from going down
- Denies Adware, Spyware, Viruses, and malicious software
- Identifies flaws and weaker points
- Enhances customer support for the effective security practices of the firm
- Implements powerful Cybersecurity measures to restore stolen data
- Offer firms and users in-demand privacy by defending their private details
- Reduces the system delays and failures to eliminate the jeopardy of hacking
A Cyber Security degree serves as authorization to grab a relevant job role. Here are some of the key roles of a cyber security expert:![]()
1. Cyber Security Analyst:
Implied from the name itself, the cyber security experts in this job role analyse hardware, software, and networks for testing vulnerabilities. They hold a vast knowledge of computer security that helps them to inspect tools for security and suggest recommendations on what they are implementing.
Cyber security analysts are the only professionals in small and medium-sized businesses who are imposed with the responsibility of preserving IT safety. Alternatively, they can be a part of a team in any large organisation. They are exceptionally well-versed in communication because they closely collaborate with internal and external investors.
2. Information Security Officer:
The need of information security is proliferating. Information Security Officers work as a defence between electronic data and illicit users willing to steal that data. Cyber security experts set up external barriers like firewalls and work with users to illustrate potential threats.
This job role considers the need for information security and works to prevent direct access to valuable information. The employers willing to fill vacancies for this job role often look for cyber security certification and security clearances.
3. Network Security Engineer:
These cyber security experts deal with supervising and identifying threats on a network. After the threats are detected, Network Security Engineers will create an incident response that might entail other participants of the cyber security team.
One of the prime responsibilities of a Network Security Engineer is to maintain network security. In case there is an issue, they quickly work to ensure the continued security of the network. Moreover, they hold advanced skills in handling log data and the forensic intellect to track a breach again to its source.
4. Penetration Tester:
Other names of Penetration Testers are Ethical Hackers and White Hats. These cyber security experts work like an outlaw who collaborates with the authorities to utilise their powers for enhanced cyber security. They can penetrate security systems to provide proof that vulnerabilities exist.
In a large-scale infrastructure like power grids and utility systems. The Red Teams is a group that tests an organisation’s efficiency.
5. Computer Forensics Investigator:
The major responsibility of a Computer Forensics Investigator is to recover data from the storage devices that might have been corrupted, encrypted, or influenced by a virus. They can team up with law enforcement agencies to chase cybercriminals. Alternatively, they may work for private firms that became the victims of those cybercriminals.
The rise in cyber threats has created a growing demand for skilled cybersecurity experts. As risks continue to evolve with advancements in technology, organizations need professionals trained to handle attacks effectively. Enrolling in cyber security courses online helps individuals gain the knowledge and skills required to protect systems from potential threats.
With businesses shifting towards cloud computing and digital transformation, data security has become a top priority. Organizations will require professionals who have completed the best cyber security courses to safeguard sensitive information from breaches. Investing in cyber security training ensures IT professionals stay updated with the latest security measures.
To keep up with the increasing cybersecurity threats, more IT professionals must upskill through cyber security certifications. These certifications validate expertise in handling security risks and make individuals more employable. Many online cyber security courses offer hands-on training to prepare learners for real-world challenges.
The future of cybersecurity will heavily rely on artificial intelligence (AI) to detect and prevent attacks in real time. As AI-driven security systems become more common, professionals with specialized training in this field will be in high demand. Understanding AI-based security solutions through cyber security courses can help individuals stay ahead in the industry.
Let’s understand the fundamental Cybersecurity terminologies:
1. Endpoint Security:
Endpoint security focuses on protecting endpoints so that they restrict the entry of malicious actors or access to an organisation's network. It entails various security solutions to defend against threats from remote or on-premises devices. Moreover, endpoint cyber security can assist you in ensuring endpoint compliance with the data security standards
2. Network Security:
Cyber network security safeguards the data on your network against a security breach that can result in unauthorised use or data loss. The design of cyber network security is intended to keep data secure and permit reliable access to information by different users in the network.
3. Cloud Security:
Cloud security is an assortment of technologies and processes designed to deal with internal and external threats to business security. Many organisations are looking to hire a proficient cyber security expert to assist in their digital transformation-based cyber security strategy. For Cloud security, organisations use cloud-based tools and services.
Also known as Cloud computing security, it entails protocols, policies, and controls that safeguard Cloud-based systems.
4. Application Security:
Application security refers to the security measures employed at the application level. These measures aim to protect the code or data in the app from being hijacked or stolen. Various security considerations that appear during app design and development are entailed in Application Security. Moreover, Application Security also involves strategies and systems to protect apps after deployment.
5. ICS / OT Security:
Operational Technology (OT) defines the environments consisting of Industrial Control Systems (ICS). The same incorporates Industrial Automated Control Systems (IACS), Process Control Networks (PCN), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA).
6. Automotive Security:
Automotive security is the branch of computer security working on cyber risks associated with the automotive industry. The demand for Automotive Security stems from the increasing number of ECUs in vehicles and the use of various forms of communication to and from the vehicle wirelessly and remotely.
7. Mobile Security / BYOD:
Software updates for mobile devices help your employees ascertain that all devices they use at work have the latest security.
BYOD (Bring your own device) implies the trend of employees who use personal devices to link to their organisational networks and access business-centric systems and confidential data.
The following terminologies can help you practice good cyber security habits:![]()
1. Encryption:
Encryption in cyber security implies the encryption and decryption of the encrypted language. Only the sender and the anticipated recipient can decrypt it to ensure safe data transmission. In other words, it is a prevention mode using which parties restrict access to information by unsolicited parties.
2. Device protection:
Cyber security not just protects digital data but also protects your physical devices.
The best practices listed below assist you in protecting your devices against cyber risks:
- Backup your data
- Password-protect your devices
- Lock your device when not in use
- Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for VPN Access and Remote Access to workplace systems/network
3. Back up your information:
In Cybersecurity, backing up your information implies the use of preventive measures to protect your data against unsolicited threats. These threats are not any kind of penetration, attack, or defensive system but merely back up your essential data at some other location.
4. Social media awareness:
Spreading social media awareness keeps individuals and organisations informed about how to stay protected from cyber threats. Here are the tips to spread social media awareness regarding cyber security:
- Setup a formal training program
- Implement a dedicated social media policy
- Use a social media monitoring tool
- Implement a social media security policy
- Provide social media training for new personnel
- Implement a reporting system
- Implement an incident response plan
- Conduct regular meetings
After you have gone through the above sections, there is no need to explain cyber security. Pursuing online cyber security courses not just guarantees a certificate in cybersecurity but also the following benefits too:
1. Effective focus:
- One of the key benefits of pursuing cyber security training online is that it allows candidates to focus entirely on learning.
- Since it can be pursued from anywhere, there are fewer distractions. This flexibility ensures that students can concentrate on the course material without external interruptions.
- If there is a portion of the course that seems difficult to understand, candidates can revisit it at their convenience.
- Unlike traditional classes, where the instructor moves on to new topics quickly, online learning allows students to grasp each concept thoroughly.
2. Time-saving and flexible:
- The best cyber security courses online offer unmatched flexibility.
- Since students can learn from any location, they save valuable time and money otherwise spent on commuting for offline classes.
- Depending on the selected program, candidates have the freedom to choose their study schedule as per their availability.
- This improves concentration and ensures an efficient learning experience.
3. More time to learn from instructors:
- Enrolling in an offline cyber security training program often means being part of a large group, limiting one-on-one interaction with instructors.
- However, online cyber security courses offer options for personalized learning, where students can either attend one-on-one sessions or join smaller study groups.
- With online training, students can better understand complex cybersecurity concepts and terminologies.
- If they have doubts, they can seek direct assistance from instructors, making the learning process more effective.
4. Constant updates:
- Opting for cyber security certifications through online programs ensures access to updated course content.
- Since cybersecurity threats evolve rapidly, leading institutes frequently revise their curriculum to include the latest security strategies.
- This helps students stay updated with the most recent cybersecurity trends and technologies, making them industry-ready.
5. Cost-effective:
- Compared to offline courses, cyber security course fees for online programs are generally more affordable.
- Digital resources such as video lectures, PDFs, and e-books replace physical textbooks and workbooks, reducing additional costs.
- Despite the lower fees, online courses provide high-quality education, ensuring students get the best learning experience.
6. Spontaneous adjustments for classwork:
- During cyber security courses online, students may come across topics that require extra attention.
- Online learning allows for spontaneous classwork adjustments, enabling students to spend more time on difficult subjects without falling behind.
- Even with these adjustments, the course is designed to be completed within the agreed timeframe.
- This ensures a smooth learning journey while allowing students to master challenging concepts.
- Fundamentals of Cyber Security
- Software Applications
- Physical Security & Its Importance
- Mobile Security & Common Vulnerabilities
- Network Security, Cloud Security, and Application Security
- Critical Security Components
- Malware Analysis
- Types of Cyber Attacks and Prevention Tips
- Digital Forensics
- Basic Dynamic Analysis
- Network Programming
- Network Security & Hacking
- Data Security and Recovery
- Web Application Penetration Testing
- IT & Cyber Law
- Cryptography and Encryption
- Cyber Risk & Cyber Insurance
- Importance of Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Dark Web & Deep Web
- Cyber Security Design & Maintaining Proper Resilience
Per PWC, the cybersecurity market grows at a multifaceted yearly growth rate of 15.6%, from 1.97 billion USD in 2019 to $3.05 billion by 2022. As per the research report ‘Cybersecurity Market with Covid-19 Impact Analysis’ published by Markets and Markets, the global cybersecurity market size is expected to increase from 217.9 Billion USD in 2021 to USD 345.4 Billion USD by 2026.
As per Grand View Research, the cybersecurity market attained a $179.96 billion value in 2021. It is anticipated to rise to $372.04 billion by 2028.
Factors that will drive the development of the global cybersecurity market:
- The increasing number of data breaches and cybercrimes leading to cyber security challenges
- Development of Ransomware
- Exploring new security internet threats and attack vectors
- Enhanced rate of business organisations capitalising on cybersecurity
- Rising global demand for cybersecurity professionals
- The advent of Disruptive Technologies like Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Rising sophistication in cyber threats
The Cybersecurity field is evolving, requiring professionals to upgrade their skills through cyber security training. Staying updated is essential to tackle cyber threats, and cyber security courses online provide real-time learning to enhance expertise.
With industries relying on cyber security solutions, the demand for cyber security courses in India is growing. These courses help professionals safeguard personal and organizational data from cyberattacks.
Companies seek experts with cyber security certifications to protect against hackers stealing sensitive information. Pursuing the best cyber security courses enhances career prospects and strengthens security skills.
While some enter the field without formal education, a diploma or degree in cyber security courses improves job opportunities. Certified professionals are preferred for their expertise in handling security challenges.
A well-structured cyber security training program covers Cloud Security, Threat Intelligence, and Risk Management. Flexible cyber security courses online offer in-demand skills at affordable cyber security course fees, making them a great career investment.
In India, a Cyber Security Specialist's average annual salary is INR 11 lac per annum
The salary of a Cyber Security Specialist in India can differ based on multiple factors. The following section outlines a few factors:
- Salary based on Employer
- Salary based on experience
- Salary based on the job location
1. Salary based on Employer:
Employer | Average Salary (per annum) |
Cognizant Technology Solutions | INR 10,44,162 |
HCL Technologies | INR 6,14,516 |
BT | INR 12,00,000 - INR 13,00,000 |
Source: Glassdoor
2. Salary based on experience:
Experience | Average Salary (per annum) |
1-4 years | INR 307,034 |
5-9 years | INR 540,361 |
10 to 15 years | INR 829,081 |
3. Salary based on job location:
Job location | Average Salary (per annum) |
Bangalore | INR 2,182,678 |
Pune | INR 2,137,764 |
Mumbai | INR 2,000,000 |
Chennai | INR 1,900,000 |
Hyderabad | INR 1,600,000 |
The starting salary of a Cyber Security Specialist in India is INR 253,702 per annum
The salary of a Cyber Security Specialist Abroad is $85,395/year.
Factors on which a Cyber Security Specialist Abroad salary depends:
The salary of a Cyber Security Specialist Abroad depends on many factors, some of which are discussed below:
- Salary based on job role
- Salary based on Employer
- Salary based on the job location
1. Salary based on job role:
Job role | Average Salary (per annum) |
Cyber Security Architect | $137,857 |
Web and Cyber Security Specialist | $119,000 |
Source: Salary
2. Salary based on Employer
Employer | Average Salary (per annum) |
SAP | $638,295 |
ACI Federal | $$155,328 |
Criterion Systems, Inc. | $$142,637 |
BCS Automotive Interface Solutions | $141,543 |
TRI-COR Industries, Inc | $114,069 |
ProSidian Consulting, LLC | $119,846 |
Milbank LLP | $111,539 |
TELEFONICA TECH INC. | $98,487 |
Global Connections to Employment | $95,860 |
RAMSOFT IT SERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED | $51,460 |
Source: Salary
3. Salary based on job location:
Job location | Average Salary (per annum) |
Washington, DC | $127,545 |
Fort Meade, MD | $125,142 |
Alexandria, VA | $110,879 |
Arlington, VA | $109,142 |
Atlanta, GA | $106,858 |
Scott AFB, IL | $98,232 |
Lackland AFB, TX | $96,091 |
Norfolk, VA | $95,221 |
Indianapolis, IN | $93,578 |
Source: Indeed
The starting salary of a Cyber Security Specialist Abroad is$78,976/year.
Online Cyber Security Courses Instructors
Learn From The Best
Learn from industry leaders in our computer software engineering courses and gain insights into cutting-edge tech. Learn from the best to be the best.
3
Instructors

Sidharthan Rajendran

Software Engineer
Siddharthan is striving Software Professional with experience of 8 years working with Enterprise applications in scale.

Vighneshwar Bhat

Software Engineer
Vighneshwasr is having 9+ years of experience in software development. Solid experience in developing scalable, secure products/applications… Read More

Mohinish Kant Joshi

Senior Full Stack Developer
Mohinish is Full-Stack Developer with 7+ years of experience in Application Design, Development and Deployment.He is Youtube content creator… Read More
Cyber Security Training Projects
Learn by Doing
Our software engineer programs have hands-on projects to apply theoretical knowledge in industry-relevant scenarios, preparing you to tackle real-world problems
5+
Projects
Restaurant finder is a basic application that finds restaurants on the basis of their names and shows their details such as timings and menu.The aim of this project is to instill the fundamentals of software engineering. One would demonstrate the understanding of UML, testing the knowledge of JUnit and Mockito, understanding the Object-Oriented programming and following the Test Driven Development approach.
Restaurant Finder
Restaurant finder is a basic application that finds restaurants on the basis of their names and shows their details such as timings and menu.The aim o… Know More
True Value Seller is a static car selling and reselling website. It showcases different promotions and has a ‘Contact Us’ component.Upon clicking the ‘Contact Us’ button, the user is taken to another page where the contact details of the company is shown.By working on developing a simple website, one would be able to apply his/her understanding of HTML and CSS and leverage the power of Bootstrap to make web pages beautiful efficiently.
True Value Seller Website
True Value Seller is a static car selling and reselling website. It showcases different promotions and has a ‘Contact Us’ component.Upon clicking the … Know More
Mobile Cart is a simple frontend application which allows authorised users to add different mobile phones and their respective information on a website which can then be viewed by different users. The users can search for different mobile phones on the basis of name, price, brand etc. This project makes use of developer’s understanding and application of DOM manipulation in order to develop a responsive web site which reacts to user interactions to render different content.
Mobile Cart Application
Mobile Cart is a simple frontend application which allows authorised users to add different mobile phones and their respective information on a websit… Know More
The project aims to create a Phone Directory application which allows a user to add subscribers to a service by entering the subscriber’s name and phone number; and delete the subscriber if necessary. With the Phone Directory application, one can put into practice the skills and knowledge of React.js and React Hooks. While working on this project, one learns about how one can create the front-end of the application using React.js and integrate it with the back-end.
Phone Directory Application
The project aims to create a Phone Directory application which allows a user to add subscribers to a service by entering the subscriber’s name and pho… Know More
With this application, which is named BookMyMovie, users can browse upcoming and released movies; filter released movies based on certain parameters; and view details such as genre, artists and trailer of released movies. Also, registered users can book a show for a released movie. This project is aimed at developing the front end of a real-world application in React and leveraging different frontend technologies such as Bootstrap, React Hooks, to make the development process efficient.
BookMyMovie Application
With this application, which is named BookMyMovie, users can browse upcoming and released movies; filter released movies based on certain parameters; … Know More
HireWheels is a car rental service application. While developing this application, one would be able to apply the knowledge of creating entities, data access object interface, connecting the project to a database, service layer and establishing relationships between entities. After creation of data access layer and service layer, one would move on to implement a controller layer for the same and develop REST APIs performing simple CRUD operations.
HireWheels
HireWheels is a car rental service application. While developing this application, one would be able to apply the knowledge of creating entities, data… Know More
Career Outcomes for Cyber Security Certifications
Latest Industry Trends
Equip yourself with the latest strategies and insights to thrive in the ever-evolving world of tech.
Top Recruiters










Success Stories for Cyber Security Courses Online
What Our Learners Have To Say
I got a good grasp at different technology stacks in the process of learning
The instructors, mentors were really helpful throughout the journey. The hands-on projects were a big boon to the whole process. Career coaching is as helpful as the whole journey was. Information regarding each and every aspect is provided in a proper way and he guidance is really helpful.

Punam Nandi
Senior Analyst - Software Developer
3 Years of Experience
Explored other technologies and languages that I was not working on
upGrad gave me confidence that I possess knowledge on multiple other technologies. Along with these, I was also learning some tools related to my integration background which helped me clear the interviews. It would definitely help me in acceleration of improving the profile and also the guidance on how to chose the right path

Venkatesh Yedururu
Senior Developer
5 Years of Experience
upGrad has designed a very beautiful course
Content is really good, starting from basic till advanced, the course covers all the aspects. Live lectures are add ons! Just by following the schedule and doing timely submissions, the complete course was easily manageable alongside my IT job. In my initial few months of the course, I got visible career growth. And even before completing the course, I got a job switch with 3x salary. I am very happy about my career growth within a year and continuing my Master's with upGrad to reach more heights! I used upGrad's career coaching tools to the fullest including Resume builder, Job portal, Job description to Our resume match with AI, Resume keywords, and other portals. Also, the modules created on various topics were really helpful. For example, How to enhance your LinkedIn profile, Communication skills, What to answer in interviews, and many more. One-to-one Buddy support and Recommended job openings are plus points. I would like to thank upGrad for all the help throughout the course!

Shambhavi Deshmukh
Senior Software Engineer II
4 Years of Experience
I am really thankful to upGrad for the wonderful training to upskill myself!
Thanks to Vrinda Bhaskar for all the career support and guidance. #placements #career #training

Abhinav Bhardwaj
Cyber Security Analyst
Fresher
Free Cyber Security Certification Courses
Start Learning For Free
Begin your Software Development journey with our free software development classes, a perfect starting point for upskilling in the tech domain.

Free Certificate
JavaScript Basics from Scratch
Kickstart your journey in web development by learning the basics of JavaScript including topics like datatypes and variables, conditional statements, loops & arrays.
19 Hours

Free Certificate
Data Structures and Algorithm
In this course, you will learn time complexity analysis, basic data structures like arrays, queues, stacks, and algorithms such as sorting and searching.
50 Hours

Free Certificate
Core Java Basics
Learn the fundamentals of programming with Java by exploring topics such as data types and variables, conditional statements, loops and functions
23 Hours

Free Certificate
Blockchain Technology: A Quick Introduction
Learn about the fundamentals and evolution of blockchain with the bitcoin blockchain network.
14 Hours
Cyber Security Blogs
You Might Like To Read

Are you confused about making a computer science project? Check out this article to find top 12 interesting and creative project ideas.

Pavan Vadapalli

Click here to find some unique and impressive ideas for final year projects that are very useful for those studying computer science and related subjects

Rohan Vats

Looking for projects that will help you strengthen your tech career? We have curated a list of the top 10 minor project topics that will help you develop the required skills.

Pavan Vadapalli

Are you looking for suitable engineering projects? Final year students and young professionals can choose from these trending topics to be industry-ready!

Rohit Sharma

When two classes, modules, or components have low dependencies on each other, it is called loose coupling in Java.

Rohan Vats

Discover top robotics projects and ideas for beginners and intermediates, learn about their learning outcomes, and understand the importance of robotics skills in the job market.

Pavan Vadapalli

In this post, we're going to discuss the trending technical courses for IT jobs. Technical courses are designed to provide knowledge to aspirants.
_upGrad Dweb-5e9cf18bbadd4ab1bd5c9ae20e34e9a6.svg)
upGrad
Learner Support and Services
How Will upGrad Supports You
Receive unparalleled guidance from industry mentors, teaching assistants, and graders
Receive one-on-one feedback from our seasoned tech faculty on submissions and personalized feedback to improvement
Our Syllabus is designed to provide you with ample of industry relevant knowledge with examples
You can write to us via studentsupport@upgrad.com or for urgent queries use the " Talk to Us" option on the learning platform
We are always there to support our online software course learners on demand.
Timely doubt resolution by industry experts and software course peers
100% expert verified responses to ensure quality learning for all software courses.
Personalized expert feedback on all the online software course assignments and projects
Regular live sessions for our online students by experts to clarify concept-related doubts
FAQs on Cyber Security Courses
The critical components of Cybersecurity are Information protection, Network safety, Security in the workplace, Application safety, End-user training, and Planning for Business Continuity.
The best cyber security courses depend on your career goals and expertise level. Popular options include Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), CISSP, and CompTIA Security+. Many online cyber security courses offer hands-on cyber security training, covering ethical hacking, network security, and risk management.
Most cyber security courses online are open to graduates in IT, computer science, or related fields. However, even beginners with an interest in cybersecurity can enroll in basic courses. Advanced programs and cyber security certifications may require prior knowledge of networking and programming.
The most common kinds of cybersecurity attacks are Malware, Cross-Site Scripting (Cross-Site Scripting) (XSS), Attacks on SQL Injection, denial-of-service attacks (DoS), attacks by a Man-in-the-Middle, phishing in cyber security, Reusing Credentials, and Hijacking a Session.
A firewall is a network-based digital security system. Essentially, it is a device that supervises and regulates network traffic. It is deployed on the edge of any network or system. Primarily, firewalls protect your network or system against malware, viruses, and worms. Moreover, firewalls can block remote access and content filtering.


upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 10 AM to 7 PM
Indian Nationals
Foreign Nationals
Disclaimer
The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not .
























