For working professionals
For fresh graduates
- Study abroad
More
- Post Graduate Certificate in Data Science & AI (Executive)
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data Analysis
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software Development
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial Excellence
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content Creation
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Human Resource Analytics Course from IIM-K
- Global Master Certificate in Integrated Supply Chain Management
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- CSM® Certification Training
- CSPO® Certification Training
- PMP® Certification Training
- SAFe® 6.0 Product Owner Product Manager (POPM) Certification
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps
- Python Programming Course
- Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full Stack
- AWS Solutions Architect Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
- AWS Technical Essentials
- The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from Microsoft
5. Array in C
13. Boolean in C
18. Operators in C
33. Comments in C
38. Constants in C
41. Data Types in C
49. Double In C
58. For Loop in C
60. Functions in C
70. Identifiers in C
81. Linked list in C
83. Macros in C
86. Nested Loop in C
97. Pseudo-Code In C
100. Recursion in C
103. Square Root in C
104. Stack in C
106. Static function in C
107. Stdio.h in C
108. Storage Classes in C
109. strcat() in C
110. Strcmp in C
111. Strcpy in C
114. String Length in C
115. String Pointer in C
116. strlen() in C
117. Structures in C
119. Switch Case in C
120. C Ternary Operator
121. Tokens in C
125. Type Casting in C
126. Types of Error in C
127. Unary Operator in C
128. Use of C Language
Assignment Operator in C
Assignment operators play a vital role in the C programming language, allowing programmers to assign variable values. Understanding assignment operators is crucial for mastering the art of variable manipulation in C. So, let's begin our exploration of assignment operators
This article will explore the world of assignment operators in C, exploring their various types and providing illustrative examples.
What is Assignment Operator in C?
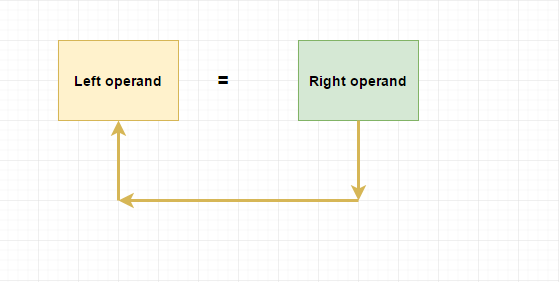
Assignment operators are binary operators in C that enable us to give values or expressions to variables. In C, assignment operators associate from right to left, resulting in the value on the right being assigned to the variable on the left. The variable is always on the left side (LHS), while the value or expression is on the assignment operator's right side (RHS).
Assignment operators have lower precedence levels compared to other operators in C. You can assign the same value to multiple variables in a single line of code, and the assignment is performed from right to left. The most basic assignment operator symbol is =, which requires two operands.
Let’s check an example of assignment operator in c -
In an expression like x = 4, the variable x is assigned 4. The variable is on the left side (LHS), and the value or expression is on the assignment operator's right side (RHS). For example:
x = 4; // Assigns the value 4 to the variable x |
The assignment operator associates from right to left. For example:
x = y = 10; // Assigns the value 10 to both variables x and y |
Here, the value 10 is assigned to y first, and then y's value is assigned to x. The simplest explanation of assignment operator associativity can be represented as:
x = (y = (10)); |
This shows that assignment operators are binary operators, requiring two operands. The LHS operand must be a variable, and the RHS operand can be a constant, variable, or expression.
List of All Assignment Operators in C
In C, we have two types of assignment operators in C: simple assignment operators and compound assignment operators.
Simple Assignment Operator (=):
A simple assignment operator assigns the value on the right-hand side (RHS) to the variable on the left-hand side (LHS)
For example:
int x; |
The value 5 is assigned to the variable x using the simple assignment operator in the above example.
Compound Assignment Operators (e.g., +=, -=, *=, /=):
Compound assignment operators combine a binary operator with a simple assignment operator. They perform an operation between the LHS and RHS, and the result is returned to the LHS.
For example:
int x = 10; |
In the above example, the compound assignment operator += adds 5 to the variable x and returns the result to x.
Compound assignment operators provide a concise way to perform an operation and assign the result in a single statement.
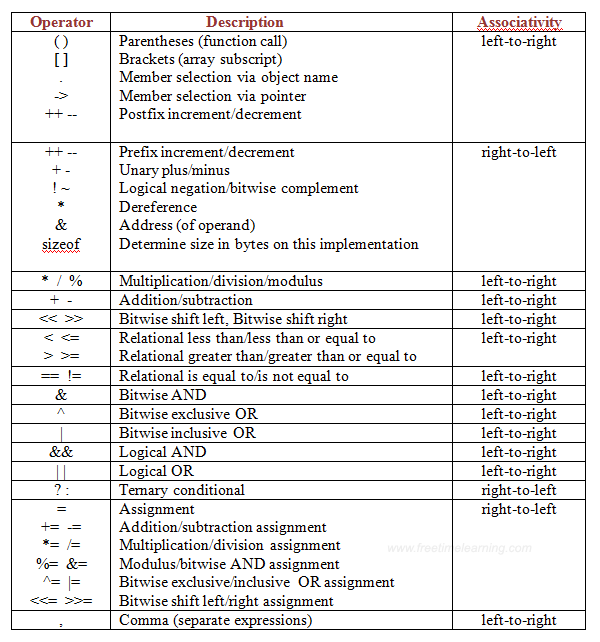
Table showcasing list of operators in C
Example Programs
Let’s look at some assignment operators' example -
Example 1: = Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 10 |
Example 2: += Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 15 |
Example 3: -= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 5 |
Example 4: *= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 50 |
Example 5: /= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 2 |
Example 6: %= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 1 |
Example 7: <<= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 40 |
Example 8: >>= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 2 |
Example 9: &= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 1 |
Example 10: |= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 7 |
Example 11: ^= Operator
#include <stdio.h> |
Output:
x = 6 |
Working Of Assignment Operators In C
Let’s understand the working of Assignment Operators in C with the help of a simple table -
Operator Name | Operator | Description | Equivalent Of | Example |
Basic Assignment | = | Assigns the value on the right to the variable on the left | NA | p = q; |
Addition Assignment | += | Adds the value on the right to the variable on the left | p = p + q; | p += q; |
Subtraction Assignment | -= | Subtracts the value on the right from the variable on the left | p = p - q; | p -= q; |
Multiplication Assignment | *= | Multiplies the value on the right with the variable on the left | p = p * q; | p *= q; |
Division Assignment | /= | Divides the variable on the left by the value on the right | p = p / q; | p /= q; |
Modulo Assignment | %= | Assigns the remainder of division to the variable on the left | p = p % q; | p %= q; |
Bitwise AND Assignment | &= | Performs bitwise AND operation on the variable with the value on the right | p = p & q; | p &= q; |
Bitwise OR Assignment | = | Performs bitwise OR operation on the variable with the value on the right | `p = p | |
Bitwise XOR Assignment | ^= | Performs bitwise XOR operation on the variable with the value on the right | p = p ^ q; | p ^= q; |
Left Shift Assignment | <<= | Shifts the bits of the variable to the left by the value on the right | p = p << q; | p <<= q; |
Right Shift Assignment | >>= | Shifts the bits of the variable to the right by the value on the right | p = p >> q; | p >>= q; |
Conclusion
Assignment operators provide various capabilities, from basic assignments to arithmetic, bitwise, and shift operations. Mastering these operators enables programmers to perform complex calculations and transformations with ease. With their concise syntax and powerful functionality, assignment operators function as a fundamental component of C programming, contributing to code readability and maintainability. The best way to hone proficiency and practical knowledge regarding the same is by upskilling, and what could be better than applying on upGrad for this!
Programming aspirants looking to master skills in software development must consider upGrad’s Executive Post Graduate Program in Software Development - Specialisation in Full Stack Development course offered under the supervision of IIIT-B. This PG program with help learners get an insight into exclusive masterclasses on GenAI, computer science fundamentals, the process of software development, building scalable websites, backend APIs, and much more. Be it a new and seasoned software developer, this program is bound to fuel your flight to success!
FAQs
1. What is the difference between simple and compound assignment operators in C?
The simple assignment operator (=) assigns the value of the right operand to the left operand. The compound assignment operators (+=, -=, etc.) perform an arithmetic operation and assign the result to the left operand.
2. Can I assign the same value to multiple variables using a single assignment statement?
You can assign the same value to multiple variables using the simple assignment operator in a single line of code, such as "x = y = z = 10;".
3. Are there any precedence rules to consider when using compound assignment operators?
Yes, compound assignment operators have lower precedence than most other operators in C. It's important to use parentheses to clarify the order of operations if necessary, especially when combining compound assignment operators with other arithmetic or bitwise operators.
-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)
Take a Free C Programming Quiz
Answer quick questions and assess your C programming knowledge


Author


Free Courses
Start Learning For Free
Explore Our Free Software Tutorials and Elevate your Career.
upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 9 AM to 12 AM (midnight)
Indian Nationals
1800 210 2020
Foreign Nationals
+918068792934
Disclaimer
1.The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
2.The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not provide any a.