Introduction
In this tutorial, we delve deep into the Python Graphical User Interface (GUI). As digital platforms evolve, the emphasis on user-centered design and intuitive interfaces is paramount. Python, with its vast ecosystem, is uniquely placed to offer developers robust tools for crafting interactive and efficient GUIs. Join us as we navigate through Python's GUI capabilities, tools, and best practices tailored for professionals aiming for excellence.
Overview
GUI, or Graphical User Interface, is an indispensable tool for enhancing user experience in applications. Python, renowned for its simplicity and versatility, provides robust solutions for GUI development. Whether you're looking to reskill or upskill, understanding Python GUIs is a valuable asset in today's digital landscape. Dive in to explore the intricacies and nuances of Python Graphical User Interface (GUI) development.
What is GUI in Python
In the digital world, a Graphical User Interface (GUI) serves as a bridge between users and electronic devices, offering an intuitive means to navigate and operate software applications. Unlike the traditional command-line approach, GUIs employ visual elements like icons, buttons, and windows to facilitate interactions. When it comes to Python—a language celebrated for its simplicity and power—the creation of GUIs is notably streamlined.
Basics of Python Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Visual Elements: These are the touchpoints where users interact. Think of buttons, menus, sliders, and checkboxes. Each element is designed to simplify user operations, allowing for a more natural interaction with the software.
- User Feedback: An essential aspect of GUIs, this ensures users are informed of their actions. Whether it's through messages, dialog boxes, or notifications, immediate feedback enhances user experience.
Python's Role in GUI
- Diverse Libraries: Python is rich with libraries and modules exclusively crafted for GUI development. Each library offers unique features catering to varied requirements.
- Cross-Platform Support: One of Python's strengths is its ability to develop applications compatible with multiple operating systems, ensuring wider reach.
Popular Libraries for GUI in Python
- Tkinter: This is Python's de-facto standard GUI library, known for its simplicity and effectiveness.
- PyQt: A robust library supporting the Qt framework, it's perfect for crafting advanced and custom GUIs.
- WxPython & PyGTK: While both cater to niche requirements, they are vital tools for developers needing specific features or compatibility.
Advantages of Using Python for GUI Development
- Swift Development: Python, with its concise syntax and a plethora of libraries, ensures rapid GUI development.
- Community Support: One of Python's greatest assets is its community. With millions of developers worldwide, finding solutions, innovative methods, or just troubleshooting becomes significantly easier.
How to Make a GUI in Python With Tkinter
Here's a basic example of how to make a simple GUI in Python using Tkinter:
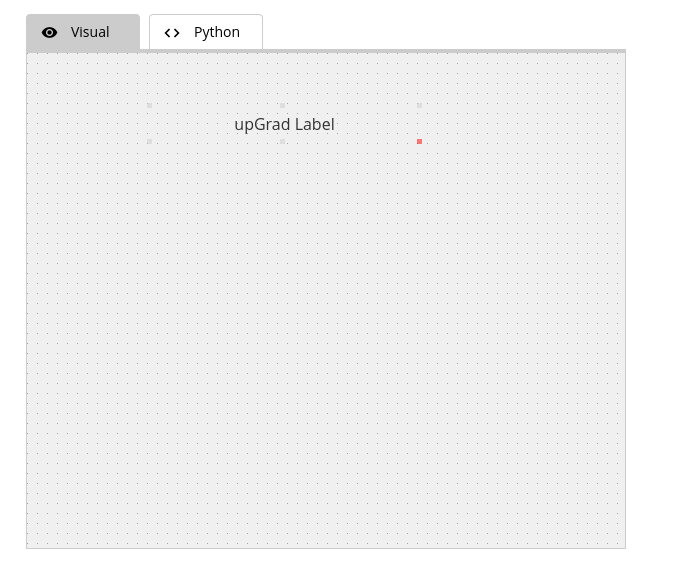
Code:
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
class App:
def __init__(self, root):
#setting title
root.title("undefined")
#setting window size
width=600
height=500
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
alignstr = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width) / 2, (screenheight - height) / 2)
root.geometry(alignstr)
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
GLabel_705=tk.Label(root)
ft = tkFont.Font(family='Times',size=14)
GLabel_705["font"] = ft
GLabel_705["fg"] = "#333333"
GLabel_705["justify"] = "center"
GLabel_705["text"] = "upGrad Label"
GLabel_705.place(x=120,y=50,width=275,height=41)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Examples of GUI in Python
Here are some more examples of GUIs in Python using Tkinter:
Button Widget
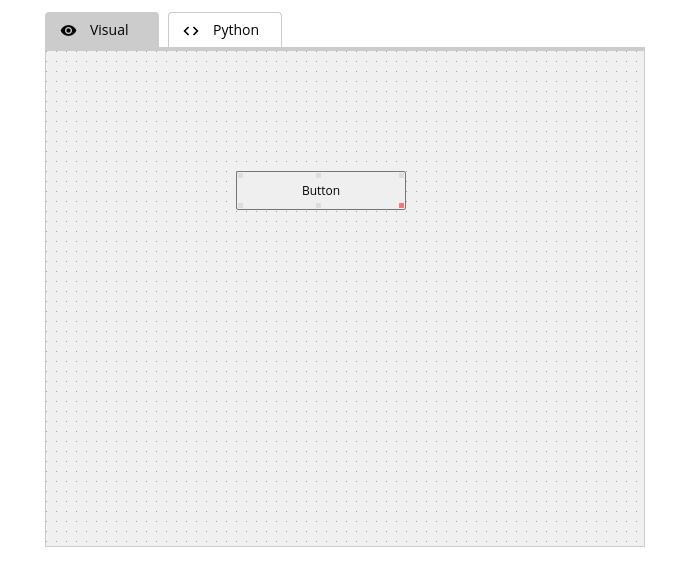
Code:
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
class App:
def __init__(self, root):
#setting title
root.title("undefined")
#setting window size
width=600
height=500
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
alignstr = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width) / 2, (screenheight - height) / 2)
root.geometry(alignstr)
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
GButton_876=tk.Button(root)
GButton_876["bg"] = "#efefef"
ft = tkFont.Font(family='Times',size=10)
GButton_876["font"] = ft
GButton_876["fg"] = "#000000"
GButton_876["justify"] = "center"
GButton_876["text"] = "Button"
GButton_876.place(x=190,y=120,width=170,height=39)
GButton_876["command"] = self.GButton_876_command
def GButton_876_command(self):
print("command")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
RadioButton Widget
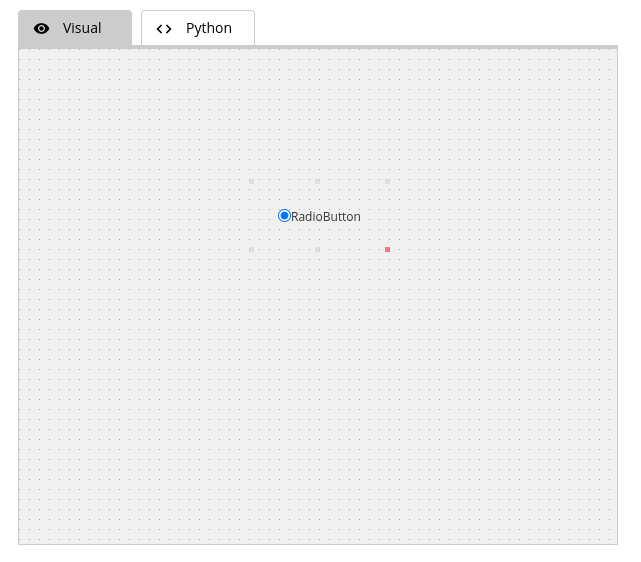
Code:
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
class App:
def __init__(self, root):
#setting title
root.title("Click Here")
#setting window size
width=600
height=500
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
alignstr = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width) / 2, (screenheight - height) / 2)
root.geometry(alignstr)
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
GRadio_737=tk.Radiobutton(root)
ft = tkFont.Font(family='Times',size=10)
GRadio_737["font"] = ft
GRadio_737["fg"] = "#333333"
GRadio_737["justify"] = "center"
GRadio_737["text"] = "RadioButton"
GRadio_737.place(x=230,y=130,width=141,height=73)
GRadio_737["value"] = "Click here"
GRadio_737["command"] = self.GRadio_737_command
def GRadio_737_command(self):
print("command")
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Listbox Widget
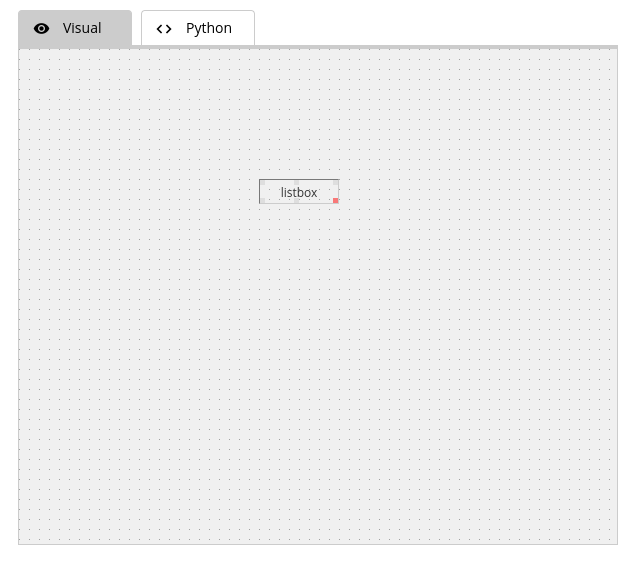
Code:
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
class App:
def __init__(self, root):
#setting title
root.title("")
#setting window size
width=600
height=500
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
alignstr = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width) / 2, (screenheight - height) / 2)
root.geometry(alignstr)
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
GListBox_152=tk.Listbox(root)
GListBox_152["borderwidth"] = "1px"
ft = tkFont.Font(family='Times',size=10)
GListBox_152["font"] = ft
GListBox_152["fg"] = "#333333"
GListBox_152["justify"] = "center"
GListBox_152.place(x=240,y=130,width=80,height=25)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Message Widget
Code:
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
class App:
def __init__(self, root):
#setting title
root.title("")
#setting window size
width=600
height=500
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
alignstr = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width) / 2, (screenheight - height) / 2)
root.geometry(alignstr)
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
GMessage_280=tk.Message(root)
ft = tkFont.Font(family='Times',size=38)
GMessage_280["font"] = ft
GMessage_280["fg"] = "#333333"
GMessage_280["justify"] = "center"
GMessage_280["text"] = "Message"
GMessage_280.place(x=100,y=100,width=345,height=135)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
There are many core widgets available for building GUIs. You can combine these widgets and use layout managers (e.g., pack, grid, place) to design more complex and interactive user interfaces in Python. Here are some Tkinter widgets you can use to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in Python:
- Button: The Button widget is used to create buttons that perform actions when clicked. You can specify a callback function to execute when the button is clicked.
- Canvas: The Canvas widget is a versatile drawing area where you can draw shapes, text, and images.
- CheckButton: CheckButton widgets allow users to select multiple options by clicking checkboxes. They are often used in settings or preference screens.
- Entry: The Entry widget is an input field where users can enter text or data. It's commonly used for user input.
- Frame: Frames are used to organize and group other widgets together. They are like containers for other widgets.
- Label: Labels are used to display text or information on the GUI. They are read-only and do not accept user input.
- Listbox: Listbox widgets display a list of items that users can select. They are useful for presenting a list of options to users.
- MenuButton: MenuButton is a widget that provides a drop-down menu when clicked. It's often used for creating menus and submenus.
- Menu: The Menu widget is used to create menus that can be attached to MenuButton widgets. Menus can have menu items with commands.
- Message: Message widgets display multi-line text messages. They are useful for displaying longer text that doesn't fit well in a Label widget.
- RadioButton: RadioButton widgets allow users to select a single option from a group of options. Only one radio button in a group can be selected at a time.
- Scale: The Scale widget provides a slider that allows users to select a value within a specified range. It's often used for adjusting settings like volume or brightness.
- Scrollbar: Scrollbar widgets are used to add scrolling functionality to widgets like Text and Listbox when the content exceeds the visible area.
- Text: The Text widget allows users to input or display multiline text. It's often used for creating text editors or displaying large amounts of text.
- TopLevel: TopLevel widgets are separate windows that can be used to create dialog boxes, pop-up windows, or additional application windows.
- SpinBox: SpinBox widgets allow users to select numeric values by clicking arrows to increment or decrement the value.
Controlling Layout With Geometry Managers
Controlling layout in a graphical user interface (GUI) is a crucial aspect of creating user-friendly and visually appealing applications. Tkinter, a popular GUI library for Python, offers three main geometry managers for controlling the layout of widgets within a window: pack, grid, and place. Here's a brief overview of each and how to make your applications interactive:
1. pack Geometry Manager: The pack manager organizes widgets in a block-like structure, placing them either horizontally or vertically. Widgets are packed into a parent widget one after the other. It's suitable for simple layouts where widgets are stacked or aligned in a single direction.
2. grid Geometry Manager: The grid manager arranges widgets in rows and columns, similar to a table or grid. You can specify the row and column where each widget should be placed. It's suitable for more complex layouts where widgets need to be aligned in a grid-like structure.
3. place Geometry Manager: The place manager allows you to specify the exact position and size of a widget using coordinates. You have fine-grained control over widget placement but need to manually specify positions. It's suitable for creating custom layouts and positioning widgets precisely.
Making Your Applications Interactive
To make your applications interactive, you can:
- Bind functions to events: Use the bind method to associate functions with events like button clicks or keypresses.
- Update widget properties: Modify widget properties (e.g., text, color) in response to user actions.
- Use variables: Tkinter provides special variable classes (StringVar, IntVar, BooleanVar, etc.) that allow you to track and update widget values dynamically.
- Create custom functions: Implement custom functions that respond to user interactions and update the GUI accordingly.
Conclusion
Python's versatility in GUI development is undeniable. From the basics to advanced topics, this tutorial aimed to present a comprehensive look at crafting intuitive graphical interfaces using Python. With a strong foundation in GUI principles and Python's powerful libraries, professionals can drive user engagement and improve overall application experiences. Before wrapping up, consider exploring upGrad's array of courses tailored for professionals like you, aiming to keep pace with industry demands. Harnessing the power of Python GUIs and mastering how to create a GUI in python can be a significant stepping stone in your upskilling journey.
FAQs
1. What are Python GUI examples?
In the Python ecosystem, GUI applications abound. For instance, calculator applications streamline arithmetic tasks with visual buttons and display panels. Text editors, with their multiple menus and formatting tools, facilitate content creation and editing. Additionally, basic games with their interactive graphics and controls are further examples showcasing the breadth of Python GUI capabilities.
2. How do you create GUI in Python?
To develop a Python GUI, one would typically leverage dedicated libraries. Among the most popular is Tkinter, known for its simplicity and being a standard library in Python. Alternatively, PyQt offers extensive tools and widgets, allowing for richer GUI designs and integrations. Both libraries come with comprehensive documentation to guide developers.
3. Are there alternatives to Tkinter for GUI in Python?
Absolutely! While Tkinter is the standard, several other potent libraries cater to varied GUI requirements. PyQt, for instance, provides tools for more advanced graphical interfaces, drawing from the Qt framework. WxPython and PyGTK, on the other hand, offer unique features and functionalities, ensuring developers have a wide palette of options for their projects.
4. Why is a GUI pivotal in software development?
At the heart of software usability lies the GUI. Graphical User Interfaces are crucial because they make applications user-friendly, translating complex operations into intuitive visual interactions. A well-designed GUI ensures that users, irrespective of their technical skill levels, can easily navigate and utilize the software, thereby enhancing user satisfaction and software adoption rates.
Take our Free Quiz on Python
Answer quick questions and assess your Python knowledge



-35c169da468a4cc481c6a8505a74826d.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)






%20(1)-d5498f0f972b4c99be680c2ee3b792d7.svg)












-d9bdeff6165f4eb1ba2adcebde78e961.svg)








-ae8d039bbd2a41318308f8d26b52ac8f.svg)






-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)






