Introduction
In this tutorial, we'll venture into the realm of what is list in Python? As dynamic arrays, lists stand at the intersection of simplicity and power in Python. Their robustness empowers developers to harness data for a plethora of applications. Read on for an in-depth analysis.
Overview
Lists, integral to Python, are mutable and ordered data structures. By supporting various data types and offering a suite of methods, they simplify data handling and provide foundational knowledge for aspiring Python developers. Keep reading to know all about what is list in Python?
What is List in Python?
At the heart of Python data structures lies the concept of lists. Think of them as versatile containers, capable of holding a medley of different data types, from numbers to strings and even other lists. They're not just about storage; Python lists come with a variety of built-in functions that empower programmers to manipulate, probe, and modify the data they hold.
- Definition: A Python list represents an ordered collection of items, where each item can be just about anything—numbers, strings, other lists, and so on.
- Creation: Formed using square brackets, lists are initialized as, my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
- Flexibility: Lists boast adaptability, with a capacity to combine integers, floats, strings, and more in a singular construct.
- Indexing: Every item in a list adheres to a definite order, identified via an index value starting from 0.
- Mutability: Their dynamic nature ensures that lists can be modified post-creation.
- Nested Lists: Multi-dimensionality is achievable with lists containing other lists, granting depth to data structures. For example: nested_list = [1, [2, 3], 4]
Example of Creating a List in Python
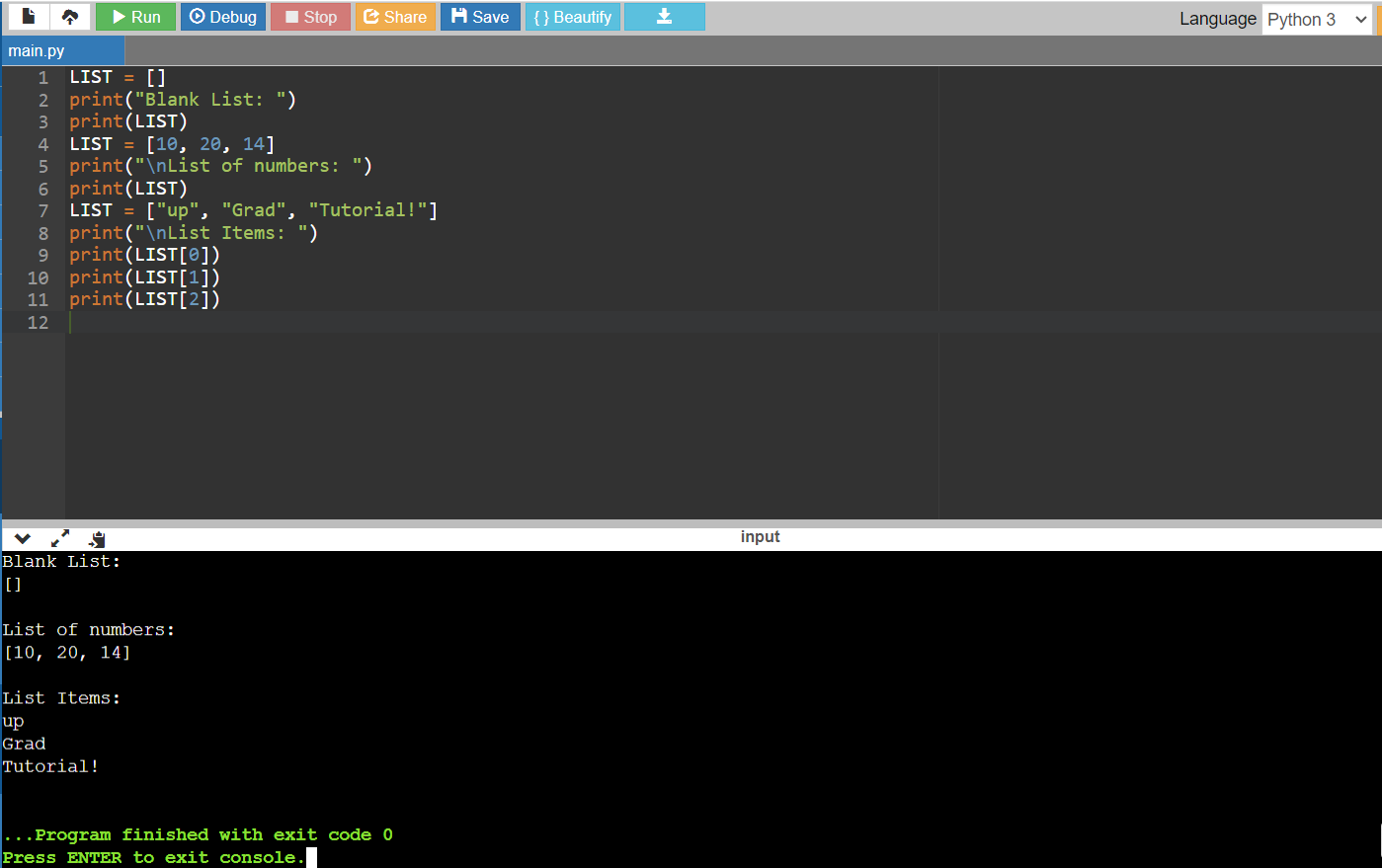
Code:
LIST = []
print("Blank List: ")
print(LIST)
LIST = [10, 20, 14]
print("\nList of numbers: ")
print(LIST)
LIST = ["up", "Grad", "Tutorial!"]
print("\nList Items: ")
print(LIST[0])
print(LIST[1])
print(LIST[2])
Python List - Characteristics
In Python's diverse ecosystem, lists hold a distinguished position due to their myriad characteristics. These versatile data structures, emblematic of Python's adaptability, are equipped with features ranging from ordered storage to intrinsic mutability. Delving into their attributes, it's evident why they're pivotal for intricate data operations and management in the programming realm. Let's take a look at some of their features:
- Ordered Collection: Unlike sets, lists preserve the order of items, ensuring consistent data representation.
- Dynamic Size: Depending on the requirements, lists can expand or contract.
- Access Methods: Leveraging both positive and negative indexing, items can be accessed. For instance, my_list[-1] fetches the last element.
- Mutability: Lists are inherently mutable, offering avenues to edit, append, or delete elements post-instantiation.
- Versatility: Alongside storing heterogeneous data types, lists can encapsulate other complex objects.
- Efficiency: Operations like appending (append()) are designed for swift execution, and optimizing performance.
- Methods: With an array of built-in functions, lists simplify data management. Examples include sort(), extend(), and insert(), among others.
Example of Accessing Elements From the List
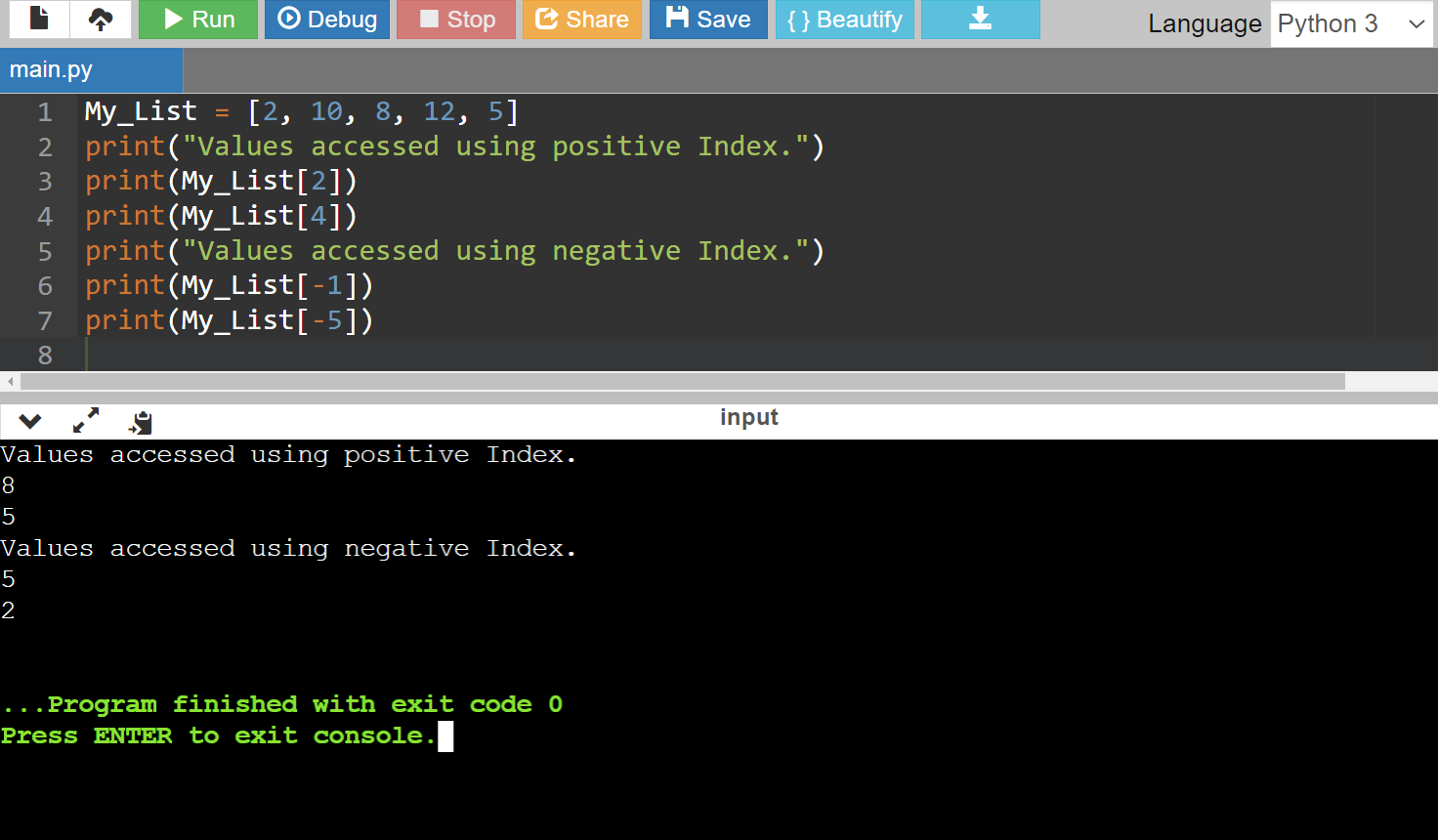
Code:
My_List = [2, 10, 8, 12, 5]
print("Values accessed using positive Index.")
print(My_List[2])
print(My_List[4])
print("Values accessed using negative Index.")
print(My_List[-1])
print(My_List[-5])
Negative Indexing in Python List
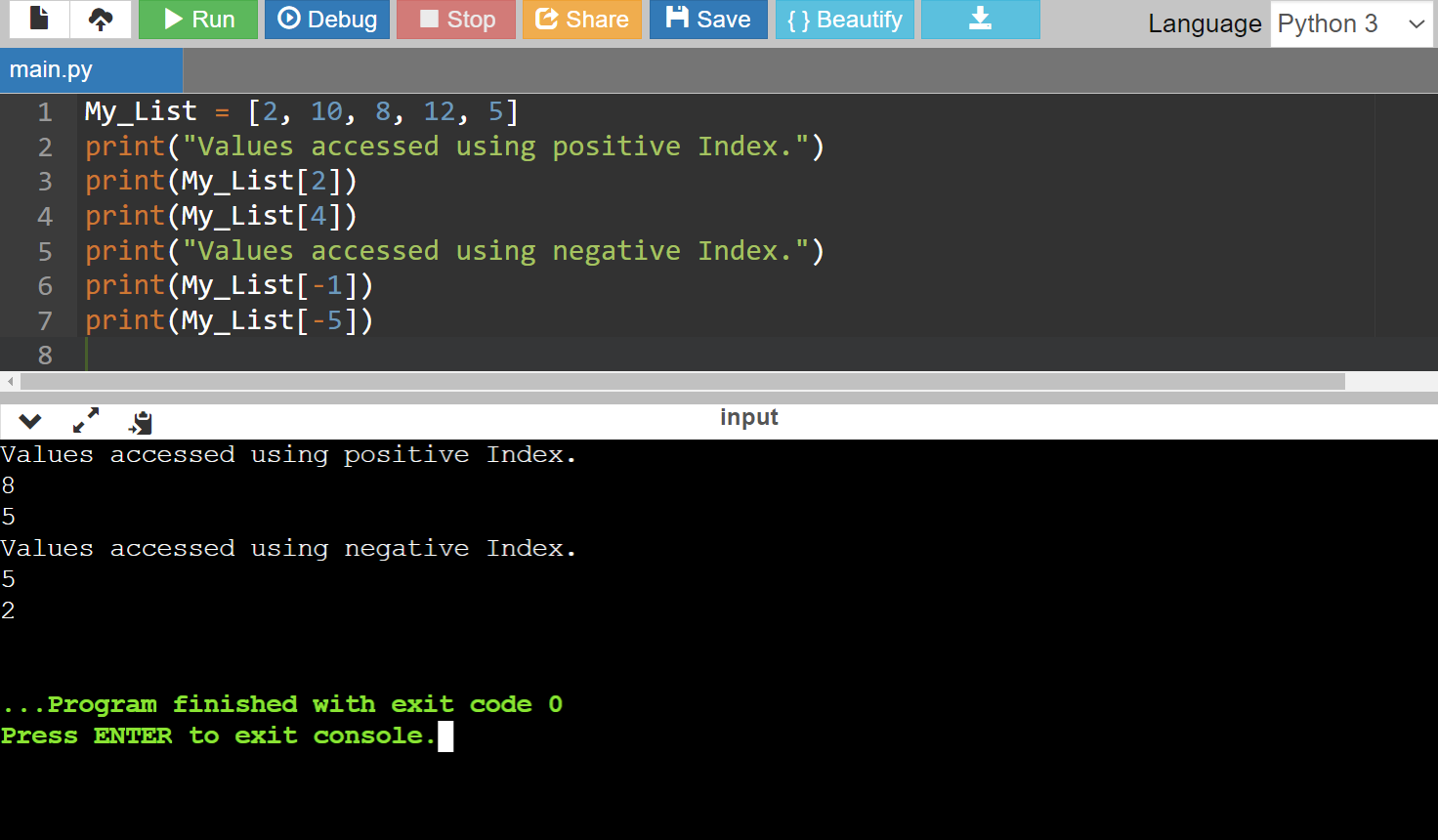
Code:
My_List = [2, 10, 8, 12, 5]
print("Values accessed using positive Index.")
print(My_List[2])
print(My_List[4])
print("Values accessed using negative Index.")
print(My_List[-1])
print(My_List[-5])
How to Get the Size of List in Python?
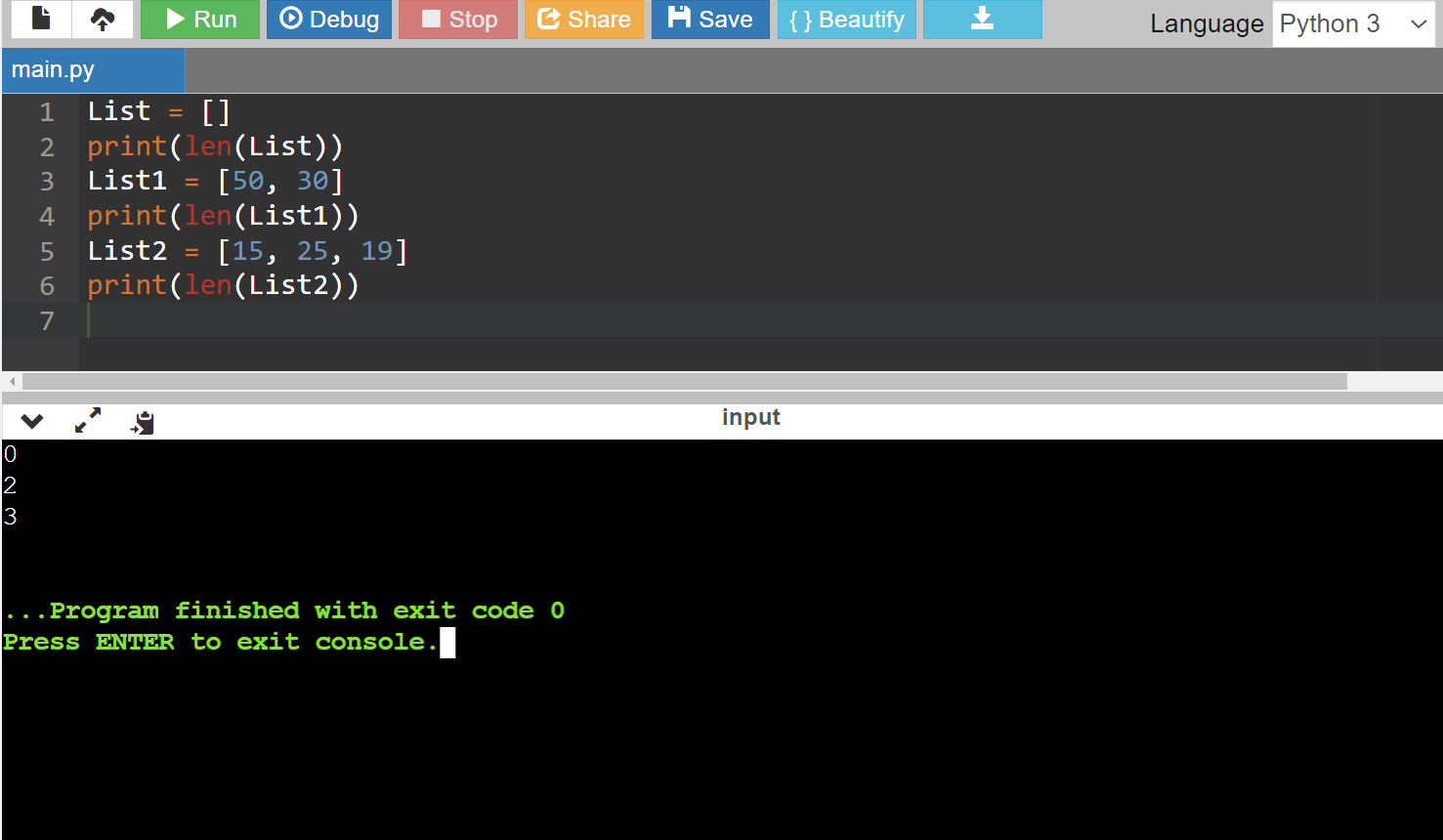
Code:
List = []
print(len(List))
List1 = [50, 30]
print(len(List1))
List2 = [15, 25, 19]
print(len(List2))
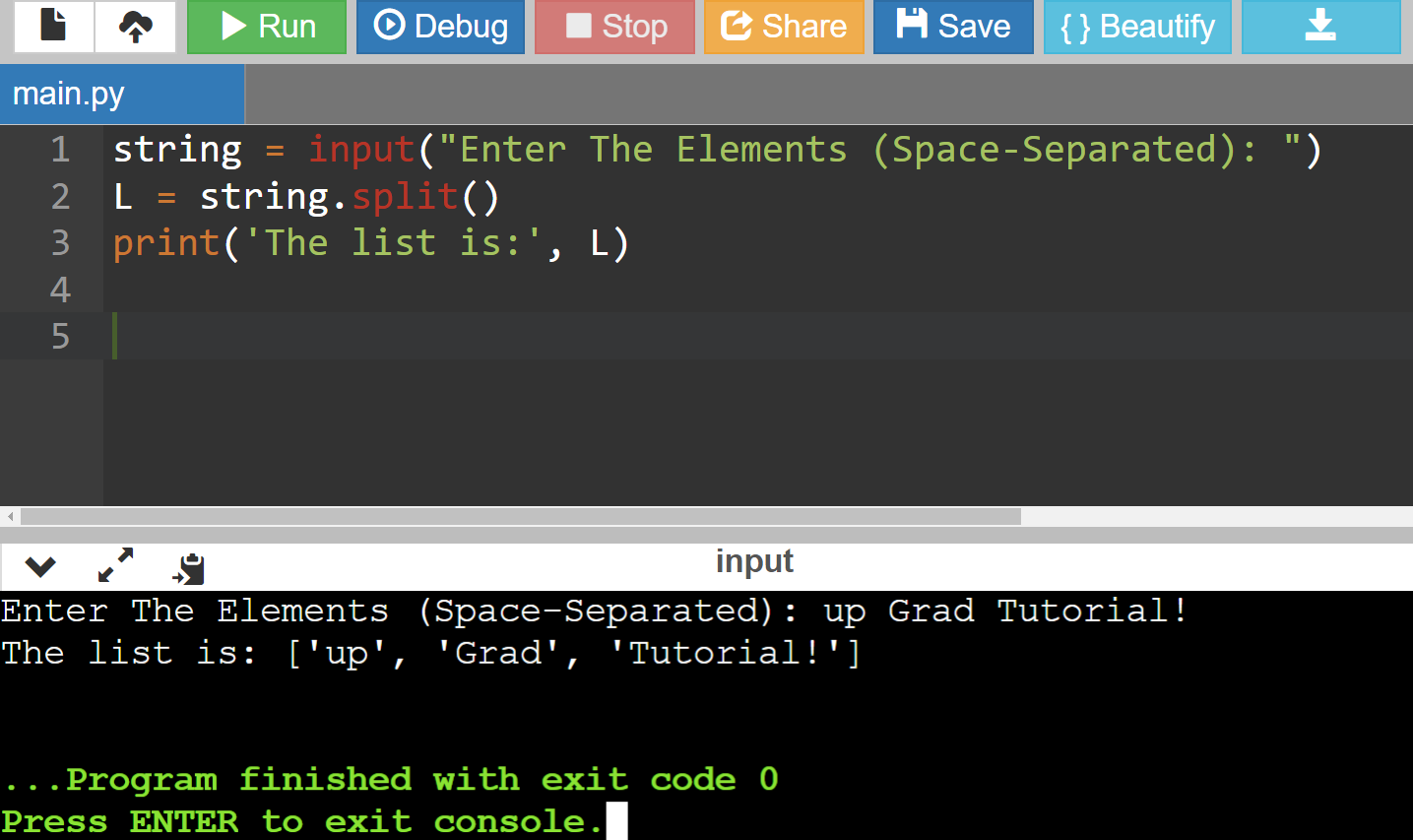
Code:
string = input("Enter The Elements (Space-Separated): ")
L = string.split()
print('The list is:', L) Adding Elements to a List in Python
Method 1: Using append() method
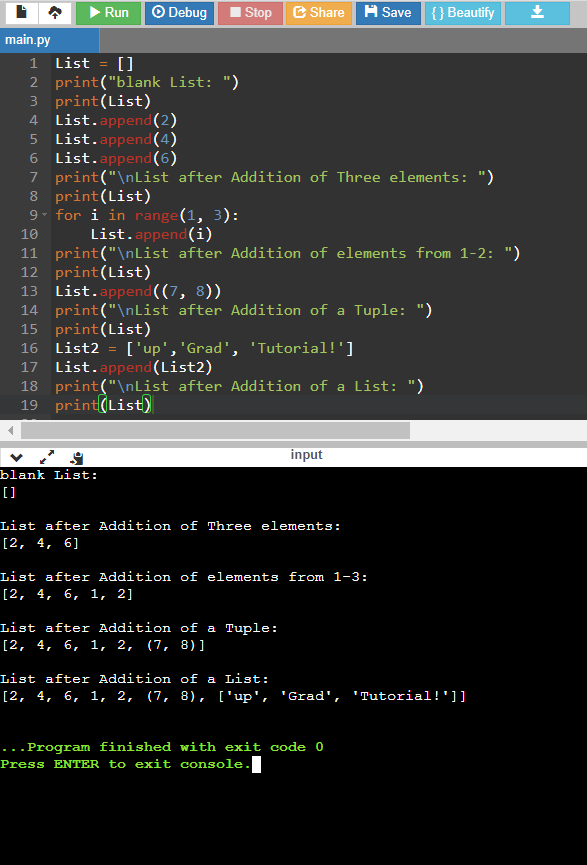
Code:
List = []
print("blank List: ")
print(List)
List.append(2)
List.append(4)
List.append(6)
print("\nList after Addition of Three elements: ")
print(List)
for i in range(1, 3):
List.append(i)
print("\nList after Addition of elements from 1-2: ")
print(List)
List.append((7, 8))
print("\nList after Addition of a Tuple: ")
print(List)
List2 = ['up','Grad', 'Tutorial!']
List.append(List2)
print("\nList after Addition of a List: ")
print(List)
Method 2: Using insert() method
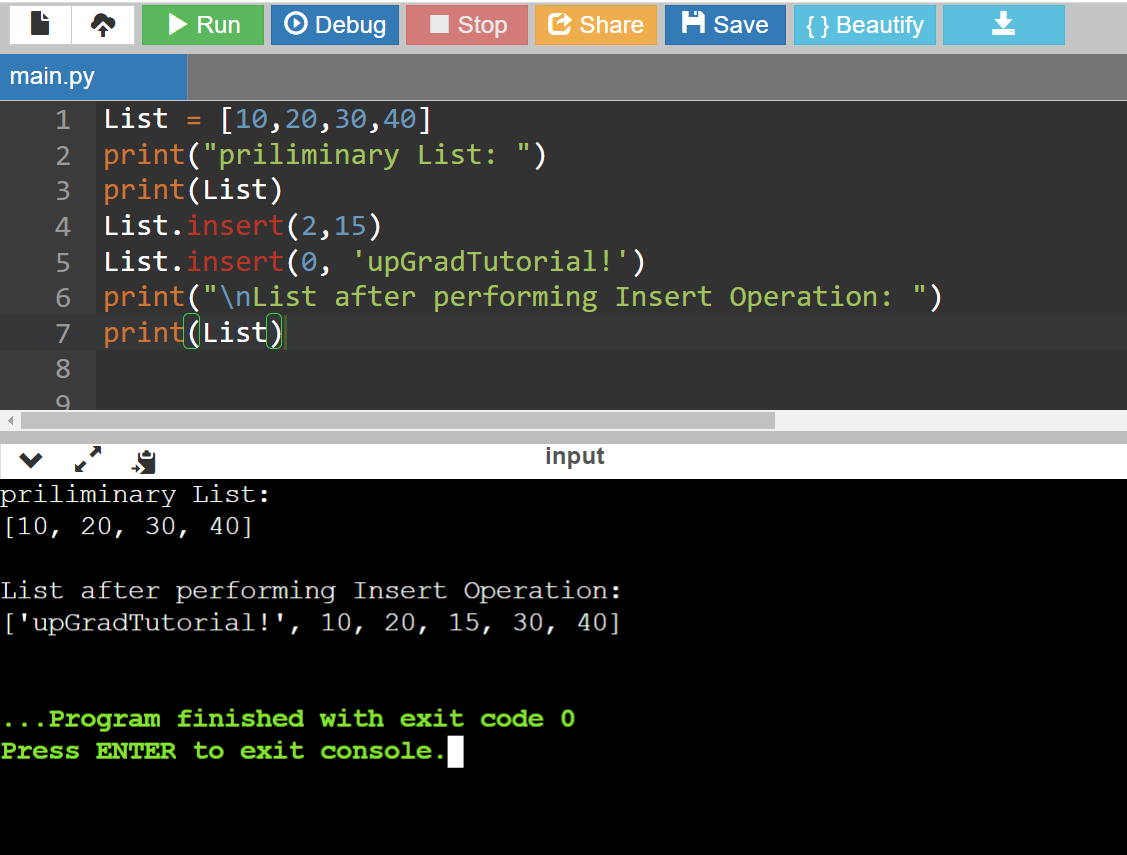
Code:
List = [10,20,30,40]
print("priliminary List: ")
print(List)
List.insert(2,15)
List.insert(0, 'upGradTutorial!')
print("\nList after performing Insert Operation: ")
print(List)
Method 3: Using extend() method
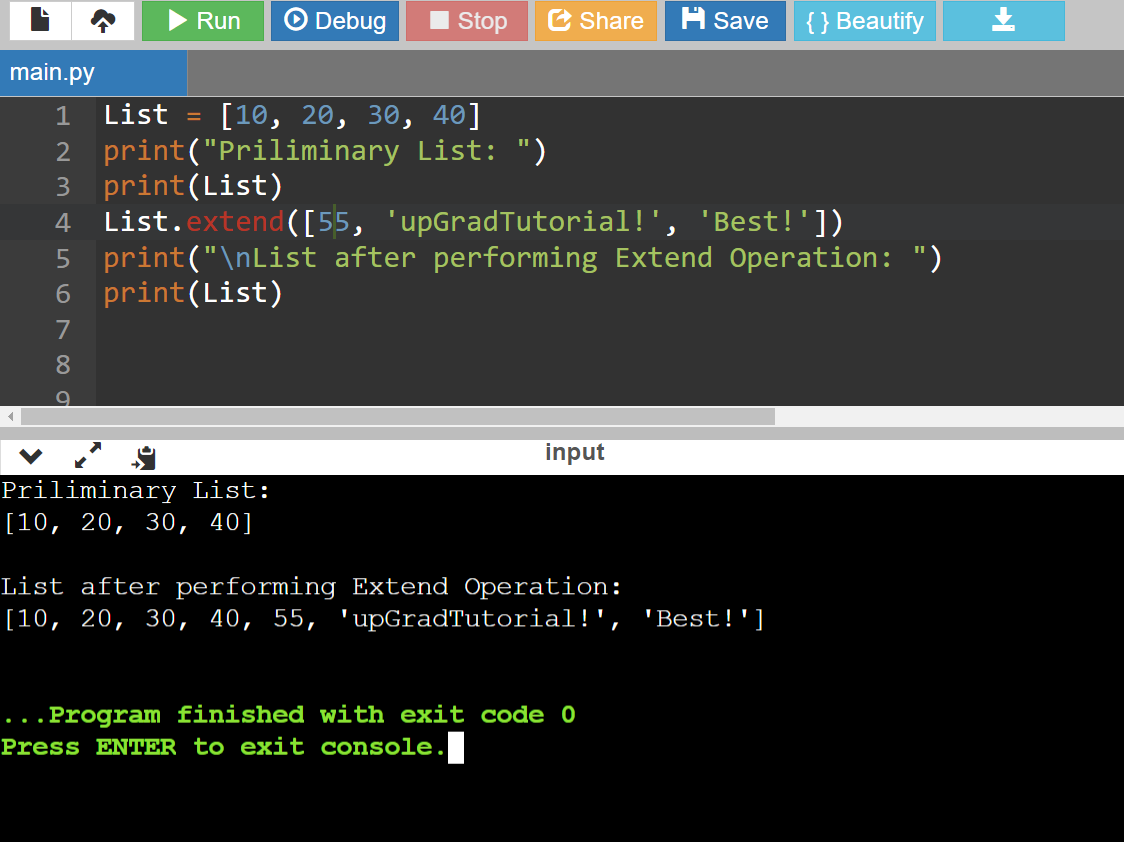
Code:
List = [10, 20, 30, 40]
print("Priliminary List: ")
print(List)
List.extend([55, 'upGradTutorial!', 'Best!'])
print("\nList after performing Extend Operation: ")
print(List)
Reversing a List in Python
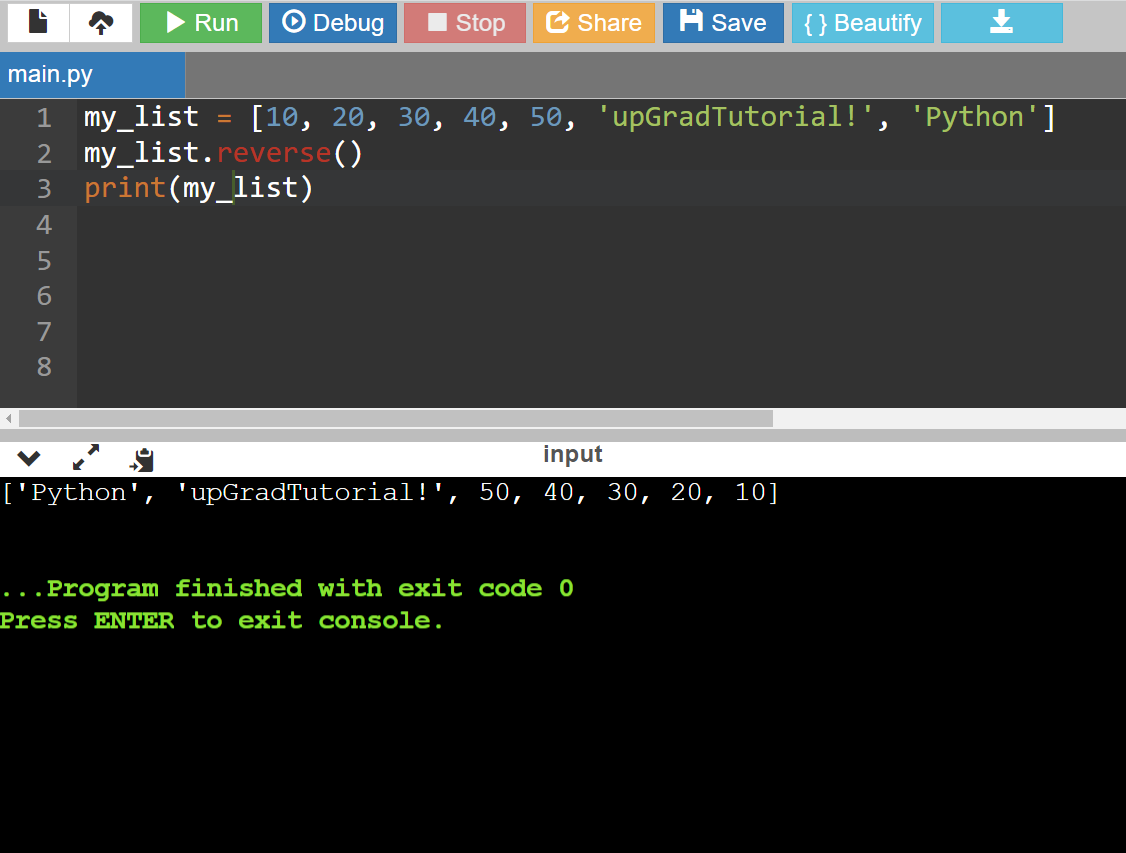
Code:
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'upGradTutorial!', 'Python']
my_list.reverse()
print(my_list)
Removing Elements from a Python List
Method 1: Using remove() method
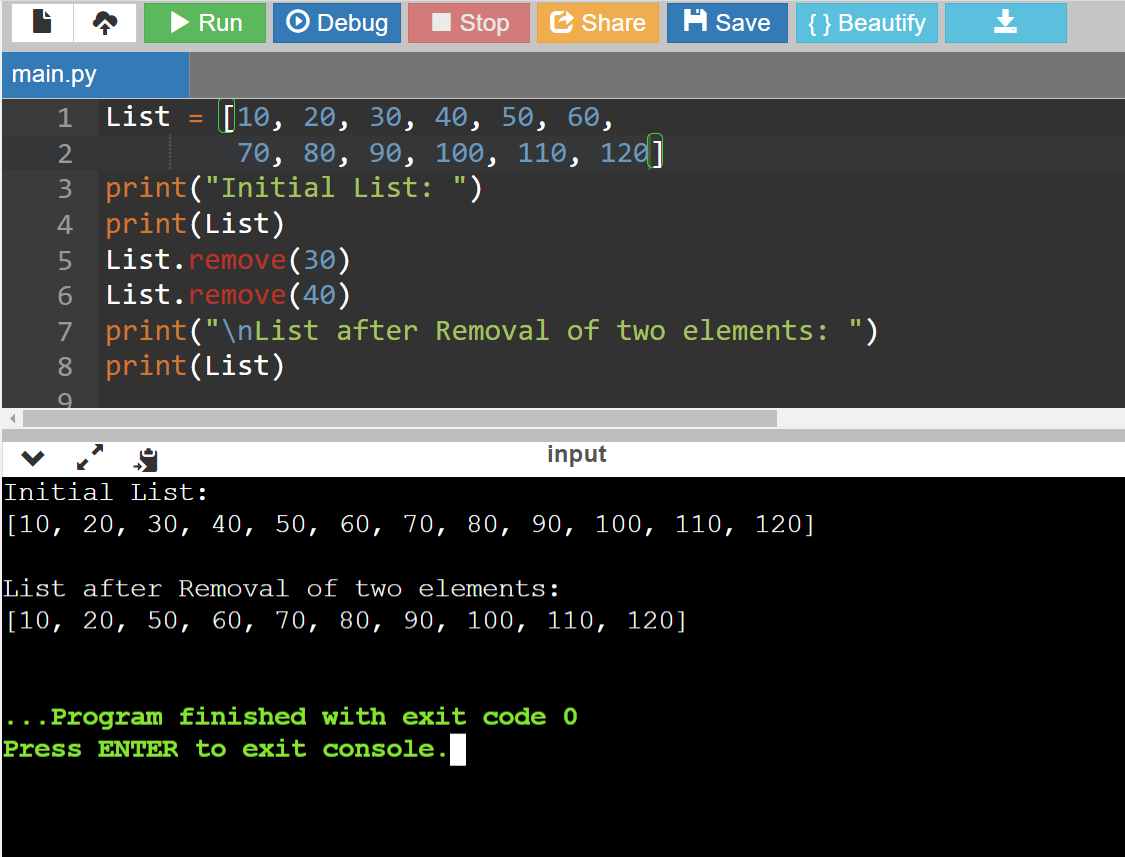
Code:
List = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60,
70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
List.remove(30)
List.remove(40)
print("\nList after Removal of two elements: ")
print(List)
Method 2: Using pop() method
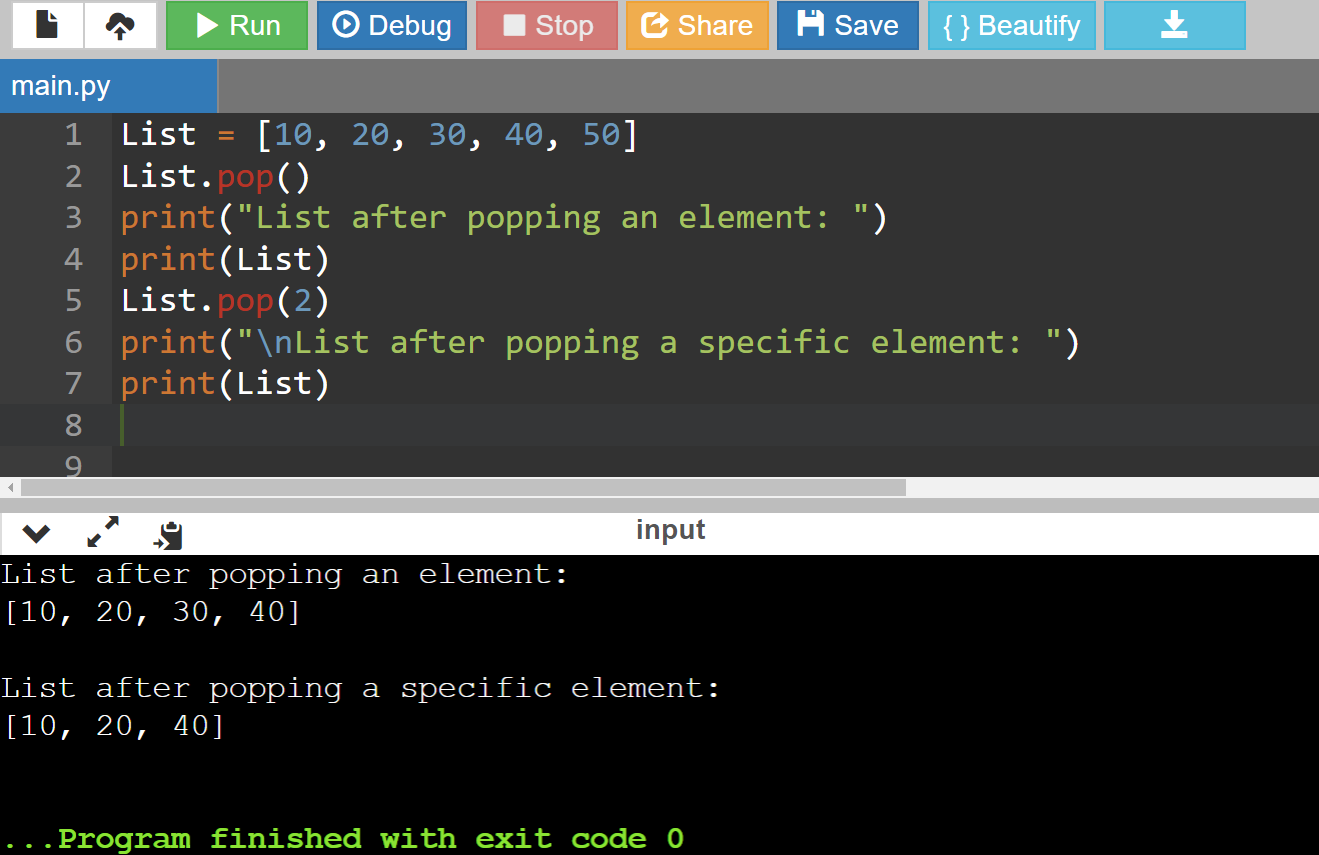
Code:
List = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
List.pop()
print("List after popping an element: ")
print(List)
List.pop(2)
print("\nList after popping a specific element: ")
print(List)
Slicing of a List in Python
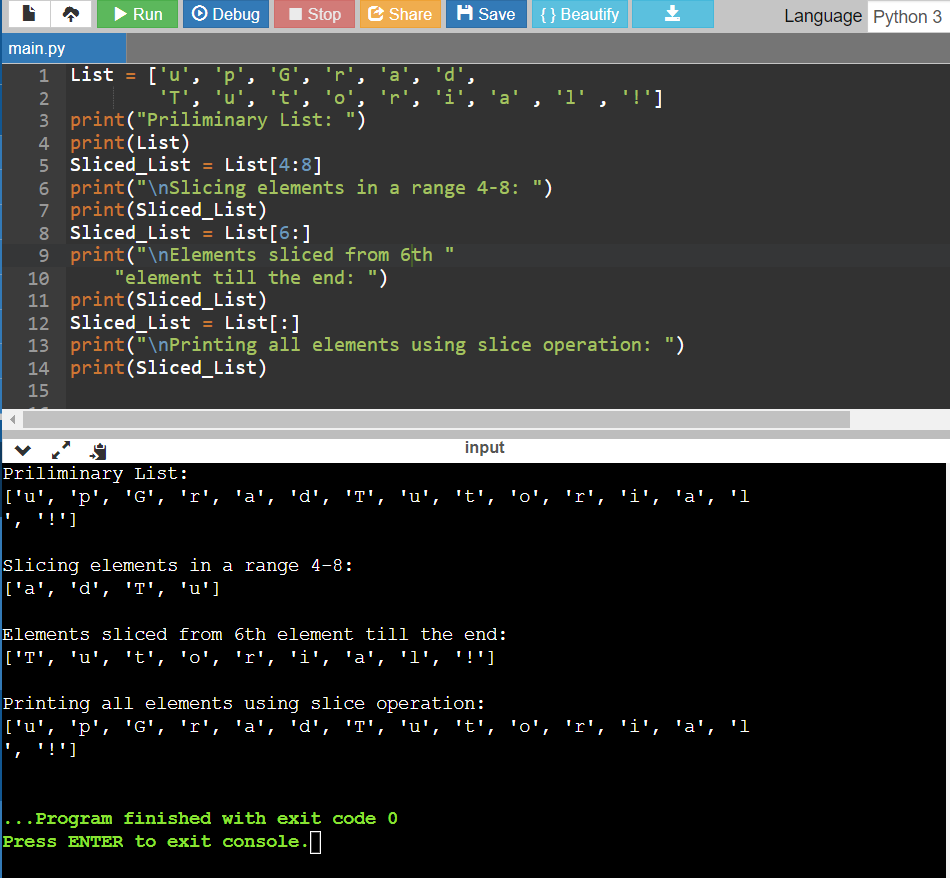
Code:
List = ['u', 'p', 'G', 'r', 'a', 'd',
'T', 'u', 't', 'o', 'r', 'i', 'a' , 'l' , '!']
print("Priliminary List: ")
print(List)
Sliced_List = List[4:8]
print("\nSlicing elements in a range 4-8: ")
print(Sliced_List)
Sliced_List = List[6:]
print("\nElements sliced from 6th "
"element till the end: ")
print(Sliced_List)
Sliced_List = List[:]
print("\nPrinting all elements using slice operation: ")
print(Sliced_List)
List Comprehension in Python
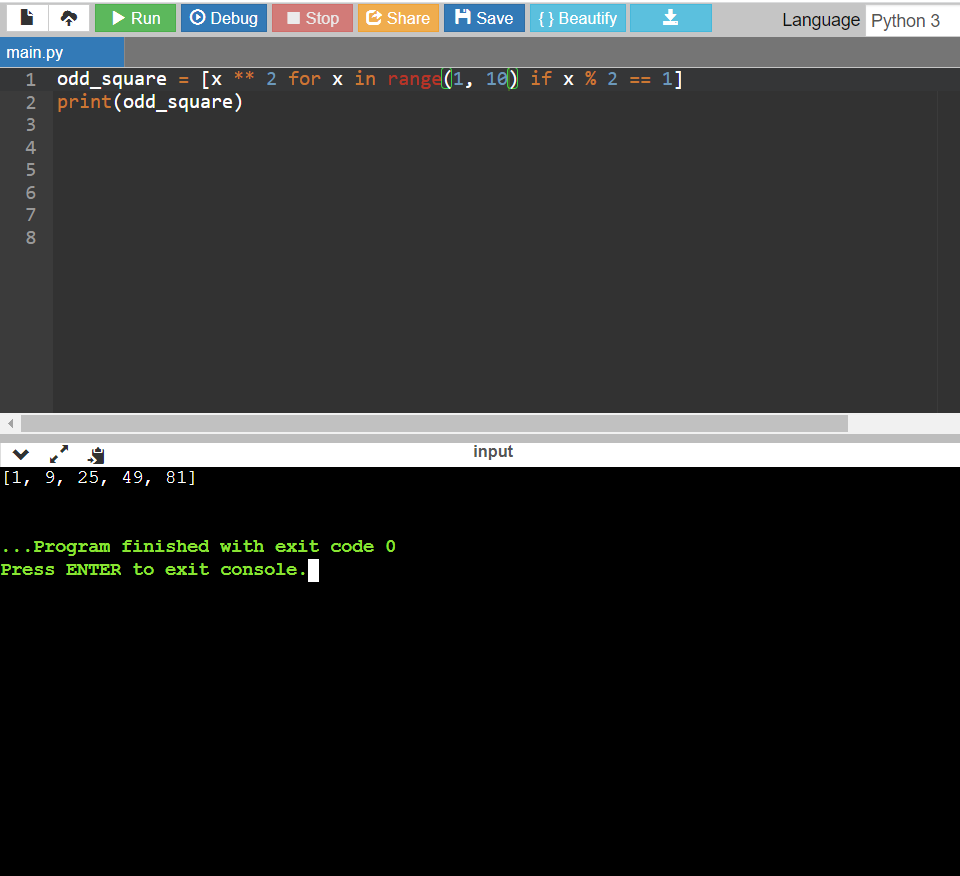
Code:
odd_square = [x ** 2 for x in range(1, 10) if x % 2 == 1]
print(odd_square)
Basic List Example in Python
Code:
# Creating a list
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange", "grape"]
# Accessing elements
print("First fruit:", fruits[0])
print("Second fruit:", fruits[1])
# Modifying elements
fruits[2] = "kiwi"
print("Updated fruits:", fruits)
# Adding elements
fruits.append("pineapple")
print("Fruits after adding:", fruits)
# Removing elements
removed_fruit = fruits.pop(2)
print("Removed fruit:", removed_fruit)
print("Fruits after removing:", fruits)
# List length
num_fruits = len(fruits)
print("Number of fruits:", num_fruits)
# Looping through a list
print("All fruits:")
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# Checking if an element is in the list
if "apple" in fruits:
print("Yes, 'apple' is in the list.")
else:
print("No, 'apple' is not in the list."
List Methods in Python
- append() - For adding an element to the ending of the list.
- extend() - For adding elements from one list to another list.
- insert() - For adding elements at the desired index positions.
- remove() - For removing the primary elements from the lists with the required values.
- pop() - For removing the elements from the required indexes within the lists, and returning them.
- clear() - For removing all elements from the lists.
- index() - For returning 0-based indexes of the first matched items. Raises ValueError if any elements aren’t found within the lists.
- count() - For returning the frequencies of elements appearing in the lists.
- sort() - For sorting the objects of the lists. It uses a compare function if passed as an argument.
- reverse() - For reversing the order of the elements in the lists.
- copy() - For returning a shallow copy of the lists i.e. two lists share identical elements via reference.
Built-in List Methods/Functions in Python
- len(my_List) - For determining and returning the lengths or sizes of the lists
- max(my_List) - For returning the elements with maximum values within lists
- min(my_List) - For returning the elements with minimum values within lists
- list(iterable) - For returning the lists containing the elements of the iterable.
- filter(function,sequence) - For testing all the elements of the list as true or not on the functions passed as arguments thereto and returning filtered iterators.
- map(function, iterator) - For returning lists after applying functions passed as arguments to all the elements of the iterables.
- lambda() - For calculating and returning the results of anonymous functions that may have any number of arguments but one expression.
- all() - For returning True if all the elements present within the lists are true or if the lists are empty.
- any() - For returning True if any of the element(s)/at least one among the items present within the list is/are true and returning False if the list is empty.
- sum() - For returning the sum of all the elements present within the list.
- reduce(func, sequence) - For applying functions passed as arguments to all the elements of the sequence and returns a result based on the function.
The Reasons Lists are Used in Python
Lists are one of the most versatile and commonly used data structures in Python. They serve various purposes and offer several advantages, which make them an essential part of the language. Here's why lists are used in Python:
- Ordered Collection: Lists are ordered collections of elements. This means the order of elements is preserved, and you can access them by their index.
- Mutable: Lists are mutable, which means you can modify, add, or remove elements after creation. This dynamic nature is useful for tasks like data manipulation and updates.
- Homogeneous or Heterogeneous: Lists can contain elements of different data types (heterogeneous) or the same data type (homogeneous). This flexibility allows you to represent diverse sets of data.
- Dynamic Sizing: Lists can dynamically change in size as you add or remove elements. This makes them suitable for situations where you need to handle varying amounts of data.
- Iterability: Lists can be easily iterated using loops, comprehensions, and other iteration techniques. This is valuable for processing each element of a collection.
- Common Operations: Lists support various operations like concatenation, slicing, sorting, and searching, making them useful for tasks ranging from simple to complex data manipulations.
- Data Storage: Lists are often used to store and manage collections of data, such as a list of names, numbers, coordinates, and more.
- Functionality: Python provides a rich set of built-in methods for lists, allowing you to perform operations like appending, extending, removing, and sorting without having to implement these functions yourself.
- Flexible Data Structures: Lists can be nested within each other to create more complex data structures, like lists of lists, which are useful for representing tables, grids, and multi-dimensional data.
- Common Usage Patterns: Lists are frequently used in loops, comprehensions, and algorithms to process and manipulate data. They are a fundamental tool for solving various programming problems.
In summary, lists are used in Python for their flexibility, versatility, and ability to handle collections of data efficiently. Whether you're working on small-scale scripts or large-scale applications, lists provide a fundamental way to organize, store, and manipulate data.
Example:
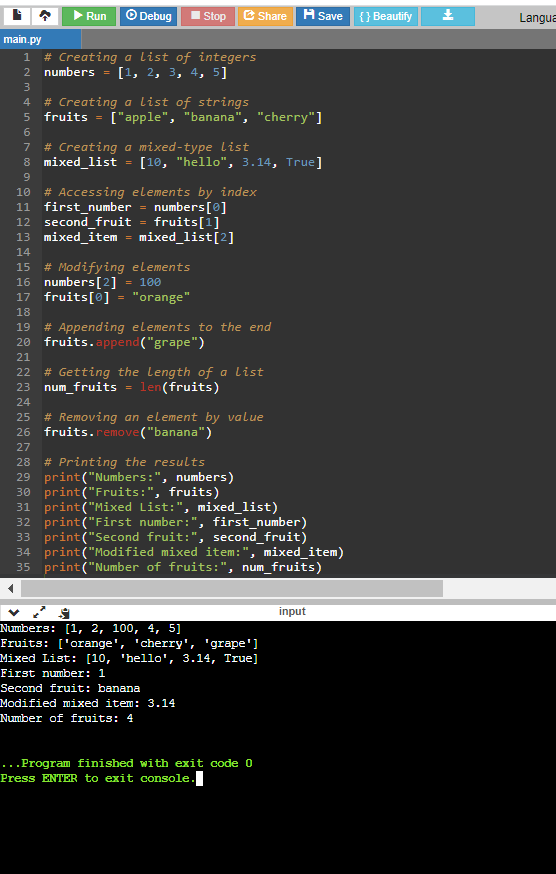
Code:
# Creating a list of integers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Creating a list of strings
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# Creating a mixed-type list
mixed_list = [10, "hello", 3.14, True]
# Accessing elements by index
first_number = numbers[0]
second_fruit = fruits[1]
mixed_item = mixed_list[2]
# Modifying elements
numbers[2] = 100
fruits[0] = "orange"
# Appending elements to the end
fruits.append("grape")
# Getting the length of a list
num_fruits = len(fruits)
# Removing an element by value
fruits.remove("banana")
# Printing the results
print("Numbers:", numbers)
print("Fruits:", fruits)
print("Mixed List:", mixed_list)
print("First number:", first_number)
print("Second fruit:", second_fruit)
print("Modified mixed item:", mixed_item)
print("Number of fruits:", num_fruits)
Conclusion
Python lists are pivotal to data science, web development, and countless other domains within programming. Their malleable nature, combined with Python's intuitive syntax, makes them invaluable. As we've delved into lists, remember that mastering them is a stepping stone to Python's broader horizon.
For those committed to diving deeper, upGrad hosts a collection of courses tailor-made for professionals. A world of knowledge awaits!
FAQs
1. What are list operations in Python with examples?
Lists support a myriad of operations. Common ones include appending (append()), removing (remove()), and iterating.
2. How do list methods in Python enhance data manipulation?
Python's list methods, from push() to pop(), streamline data handling, providing efficient pathways for operations sans external utilities.
3. Why is list slicing in Python pivotal?
Slicing grants precision in data extraction, allowing developers to capture specific segments of a list, thereby aiding in tasks like data analysis.
4. What is the difference between list and tuple in Python?
Core differences lie in their mutability. Lists can be altered post-creation; tuples cannot. This immutable nature gives tuples a unique standing in data handling.
5. Can you equate an array in Python to a list?
Both arrays and lists store collections of data. However, while lists entertain multiple data types, arrays demand homogeneity, enlisting elements of a singular type.
Take our Free Quiz on Python
Answer quick questions and assess your Python knowledge



-35c169da468a4cc481c6a8505a74826d.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)






%20(1)-d5498f0f972b4c99be680c2ee3b792d7.svg)












-d9bdeff6165f4eb1ba2adcebde78e961.svg)








-ae8d039bbd2a41318308f8d26b52ac8f.svg)















-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)






