Introduction
Ever wonder how live video streams or online games send data so quickly? The secret is often the UDP Protocol. Think of it like sending a postcard: it's incredibly fast and simple because it doesn't wait for a delivery confirmation.
This tutorial will dive into this lightweight, connectionless protocol. Understanding the UDP Protocol in computer networks is essential for anyone interested in applications where speed and low latency are more important than perfect reliability. We'll explore its core workings, key advantages, and why it's the top choice for real-time services like gaming and VoIP. Let's get started!
Stop just learning—start building. Our Software Engineering Courses give you job-ready skills with hands-on projects designed for the real world.
What is User Datagram Protocol (UDP)?
The User Datagram Protocol, or UDP, is an essential part of the Internet Protocol suite. It sits at the transport layer of this suite, the same level as the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). What makes UDP unique is that it facilitates the sending of messages, known as datagrams, from one host to another within an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
UDP is described as a 'connectionless' protocol. This term implies that unlike, TCP, it does not establish a dedicated end-to-end connection between the communicating hosts. There's no initial handshake process to set up the connection or teardown process to close it. Instead, UDP permits individual packets to be sent from one machine to another with minimal delay, which can be advantageous for certain real-time applications.
Also Read: Computer Networking Basics: Key Concepts, Types, and Benefits f Explained
Another notable characteristic of UDP is that it does not guarantee message delivery. TCP includes robust error-checking mechanisms and provisions for data retransmission if a message fails to reach its destination. However, UDP lacks these features, deliberately trading off reliability for speed. This property makes it a faster protocol and contributes to its efficiency, as less overhead is required.
UDP is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and it's not suitable for applications that require reliable, ordered data delivery, like file transfers. Where it shines is in scenarios where speed trumps accuracy. A prime example is live streaming. In such a situation, if a few data packets are dropped or arrive out of order, the impact is negligible - the key requirement is maintaining a steady flow of data. Therefore, UDP provides an essential trade-off between speed and reliability and is a powerful tool for time-sensitive applications where occasional data loss is an acceptable compromise.
Take your programming skills to the next level and gain expertise for a thriving tech career. Discover top upGrad programs to master data structures, algorithms, and advanced software development.
Why do we require the UDP protocol?
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a preferred choice for several applications and situations due to its unique characteristics. Let's elaborate on its requirements in more detail:
- Speed: The absence of error-checking and re-transmission of lost packets in UDP significantly boosts data transmission speed. Unlike its TCP counterpart, UDP doesn't wait for acknowledgments from the receiver end, facilitating faster data streaming. This makes UDP an ideal choice for real-time applications like video and audio streaming, online gaming, and live broadcasts where speed trumps the need for complete data integrity.
- Efficiency: UDP eschews complex handshaking procedures, which characterize TCP, reducing communication latency. This efficiency is critical in situations where quick transmission takes precedence over accuracy, like DNS queries or IoT applications where sensors send data to servers.
- Broadcast/Multicast: UDP's capability to support both broadcast (transmitting to all devices on a network) and multicast (transmitting to a selected group of devices) increases its utility in applications requiring data distribution to multiple recipients simultaneously. For example, in video conferencing or IPTV multicast, where the same data packet needs to reach multiple endpoints, UDP's multicast ability becomes invaluable.
- Stateless Nature: UDP operates in a connectionless manner, meaning it doesn't require a prior setup or teardown of a dedicated connection for data exchange. This stateless property makes UDP well-suited for simple query/response communication where session tracking isn't necessary, such as in Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
- Lightweight: Due to its minimalistic design, UDP is a lightweight protocol. Unlike TCP, it doesn't handle congestion control, flow control, or retransmission of lost packets. This makes UDP a simpler and less resource-intensive protocol, which is an advantage in systems where resources are scarce or need to be efficiently used.
- No Network Congestion: Since UDP does not have any mechanisms for handling network congestion as TCP does, it doesn't contribute to network congestion itself. This might be an advantage in certain high-speed or real-time applications where timely delivery is more critical than packet loss.
Also Read: What Is Data Communication? Types, Key Components, Careers in 2025
The UDP (User Datagram Protocol) header is a simple structure added to the beginning of a UDP datagram to provide essential information for the communication process. The header contains fields that define the source and destination ports, the length of the datagram (including the header), and a checksum for error detection.
UDP Header Format
Here are the components of the header:
- Source Port (16 bits): This field identifies the port number of the sender. It specifies the application or service on the source device that generated the UDP datagram.
Also Read: Top 20+ Networking Certifications for Your IT Career in 2025: A Complete Guide
- Destination Port (16 bits): This field identifies the port number of the intended receiver. It specifies the application or service on the destination device that should handle the UDP datagram.
- Length (16 bits): This field represents the total length of the UDP datagrams, including the headers and the data, in bytes. Since the minimum UDP header size is 8 bytes, the minimum length value would be 8.
- Checksum (16 bits): The checksum field is used for error detection. It contains a checksum value computed over the entire UDP datagram (including header and data). The checksum is calculated to help detect any corruption or errors that might have occurred during transmission.
Also Read: How Does The Internet Work?
Concept of Queuing in UDP protocol
In the context of the UDP protocol, queuing refers to the process of storing incoming UDP datagrams in a queue before they are processed or delivered to the application. Queuing is used to handle situations where the rate of incoming UDP datagrams exceeds the processing capability of the application or the system.
UDP does not have built-in flow control or congestion control mechanisms like TCP. This means that if an application is unable to process incoming datagrams as fast as they arrive, there's a risk of losing datagrams due to buffer overflows.
Queuing allows the system to buffer incoming UDP datagrams temporarily, ensuring that data is not lost even if the application or system is momentarily overwhelmed. The queued datagrams are then processed in the order they were received, reducing the risk of data loss.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Network Engineer Skills in 2025
Applications of UDP
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a critical component of the Internet Protocol Suite, and its unique characteristics make it the protocol of choice in a multitude of applications. The focus of UDP is on speed and efficiency rather than reliability, which makes it the perfect choice for applications where even a slight delay could result in a substantial drop in quality. Here are some of the major areas where UDP finds its usage:
- Live Streaming: UDP's high-speed data transfer makes it the go-to choice for live video or audio streaming and online gaming. In these scenarios, a real-time experience is of utmost importance, and a minor delay could severely impact the user experience.
- DNS Lookups: The Domain Name System (DNS) utilizes UDP for quick exchanges during simple query/response transactions. Given the transient nature of these exchanges, the stateless nature and speed of UDP make it an efficient choice.
- Network Protocols: Several essential network protocols, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Routing Information Protocol (RIP), employ UDP for their operations. These protocols value the quick and efficient data exchange provided by UDP.
- VoIP: Voice over IP (VoIP) is another key application area for UDP. In VoIP, the priority is on real-time transmission, even if that means some packets are lost or erroneous. This real-time priority is exactly where UDP shines, hence its widespread use in VoIP technology.
Also Read: What is TCP/IP Model? Computer Networking Guide
Disadvantages of UDP
While the UDP protocol is advantageous in several aspects, it's not without its drawbacks. The very features that make it useful in certain scenarios also introduce potential problems, making it ill-suited for applications where accuracy and reliability are more important than speed. Here are some of the most notable disadvantages of UDP:
- Unreliable: Since UDP is a connectionless protocol, it doesn't guarantee delivery of data packets. This absence of guaranteed delivery makes it unreliable for applications where every piece of data is critical, such as file transfers.
- No Error-checking: UDP doesn't offer an error-checking mechanism. As a result, erroneous data might get delivered to the receiver, leading to potential issues in the transmitted information.
- No Congestion Control: Unlike TCP, which has built-in congestion control mechanisms, UDP lacks these features. This lack can potentially lead to network congestion as UDP continues to send data regardless of network conditions.
- No Ordered Packets: UDP doesn't sequence the packets it delivers, meaning they might arrive at the receiver out of order. For certain types of data, such as a video file, receiving packets out of order can lead to problems in reconstructing the data accurately.
Also Read: What Is Information Technology? Types, Benefits, and Certifications
The UDP Pseudo-header is an additional conceptual header used in conjunction with the actual UDP header when calculating the checksum for error detection in UDP packets. It's important to note that the UDP pseudo-header is not actually present in the packet itself; it's used solely for checksum calculation purposes. The pseudo-header is required because the UDP checksum is calculated over not only the UDP header and data but also some fields from the IP header.
The UDP pseudo-header typically includes the following fields from the IP header:
- Source IP Address (32 bits)
- Destination IP Address (32 bits)
- Protocol (8 bits, specifying UDP)
- UDP Length (16 bits, including header and data length)
Here's a general representation of how the UDP pseudo-header is used in checksum calculation:
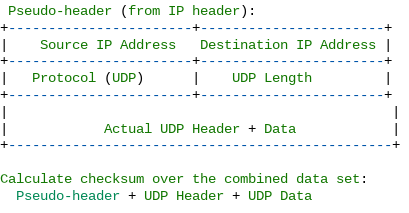
Once the checksum is calculated over this entire combined data set, it's included in the UDP packet's checksum field. When the recipient receives the packet, it can recalculate the checksum using the same algorithm and verify that it matches the received checksum. If they don't match, it indicates a possible error during transmission.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the UDP Protocol is all about one crucial trade-off: sacrificing guaranteed reliability for incredible speed.
While TCP acts like a registered letter, UDP is like a postcard—it's the perfect choice for real-time applications like online gaming and live streaming, where a lost data packet is better than a long delay. Understanding when to use the UDP Protocol in computer networks is a mark of a skilled developer, showing you know how to choose the right tool for the job. At upGrad, we focus on building this kind of practical, real-world expertise.
FAQs
1. What's the difference between UDP protocol and TCP?
While both are transport protocols, when compared to UDP protocol, TCP is connection-oriented, error-checks and ensures data delivery, but is slower. In contrast, UDP is faster, connectionless, and doesn't guarantee delivery or error-check. Can you give a UDP protocol example?
2. Can you give a UDP protocol example?
Sure! Live video streaming services often use UDP due to its speed and efficiency, which facilitates real-time experience. What is UDP protocol in computer networks?
3. What is UDP protocol in computer networks?
UDP is a protocol in computer networks that allows applications to send datagrams to other hosts on an IP network without requiring prior communications to set up special transmission channels or data paths. What are the UDP protocol advantages and disadvantages?
4. What are the UDP protocol advantages and disadvantages?
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) offers several advantages, including speed due to less overhead, efficiency because of no handshaking procedures, broadcast and multicast support, a lightweight design, and lack of contribution to network congestion. However, these benefits come with certain disadvantages, such as a lack of reliability, as UDP does not offer guaranteed delivery. Also, since UDP does not handle congestion control or flow control, it might not perform optimally in congested network environments. What is the UDP protocol number?
5. What is the UDP protocol number?
In the Internet Protocol Suite, protocols are identified by a specific number. For UDP, the protocol number is 17. This number is used in the protocol field of the IP headers to indicate the transport protocol being used. What does a UDP connection mean, considering UDP is a connectionless protocol?
6. What does a UDP connection mean, considering UDP is a connectionless protocol?
Unlike TCP, UDP is a connectionless protocol, meaning it doesn't establish a dedicated end-to-end connection between the sender and receiver before data transmission. When we talk about a "UDP connection", it generally refers to the process of a client sending a UDP message to a server with the expectation of receiving a response. This process does not involve any handshake or connection termination procedures. It's more about the logical communication between two entities rather than a physical or dedicated connection.


-35c169da468a4cc481c6a8505a74826d.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)






%20(1)-d5498f0f972b4c99be680c2ee3b792d7.svg)












-d9bdeff6165f4eb1ba2adcebde78e961.svg)








-ae8d039bbd2a41318308f8d26b52ac8f.svg)







